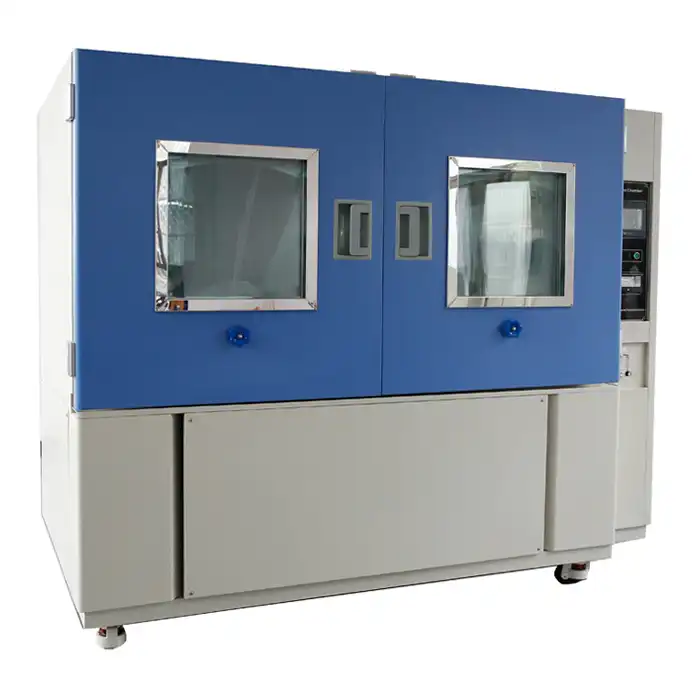
Inside the Sunshine Weatherometer: Understanding UV, Temperature, and Humidity Control
Environmental testing plays a pivotal role in predicting the long-term performance of materials. The sunshine weatherometer is an advanced tool for simulating real-world conditions, ensuring that products withstand the effects of UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and humidity variations.
Harnessing UV Radiation: Simulating Solar Exposure for Accurate Material Testing
One of the critical functions of the sunshine weatherometer is to replicate the damaging effects of UV radiation, a major contributor to material degradation. This is especially important for manufacturers developing products meant to endure prolonged outdoor exposure, such as automotive components, construction materials, and outdoor furniture.
By simulating high-intensity UV light, the weatherometer can provide accelerated testing that mimics years of solar exposure in a fraction of the time. This ensures users have reliable data on how their materials will react to sunlight, helping to prevent fading, cracking, and brittleness over time. For example, plastics exposed to UV can break down more rapidly without proper testing, leading to product failures. By harnessing this powerful tool, manufacturers can make informed decisions about the longevity and resilience of their materials, ensuring they meet quality standards.
Precision Temperature Management: Creating Realistic Climate Conditions for Comprehensive Aging
The sunshine weatherometer also plays a crucial role in replicating the thermal effects materials face in different climates. Precise temperature control is key for understanding how items will perform in environments that experience extreme heat or cold. Whether a product will be used in scorching deserts or freezing tundras, temperature fluctuations can cause thermal expansion, contraction, or other stress factors that degrade materials over time.
For instance, automotive paint exposed to high heat can start to blister or peel, while electronic components may malfunction if they cannot endure extreme temperature cycles. The weatherometer allows manufacturers to simulate these conditions, offering insights into thermal aging and ensuring that products maintain integrity even in the harshest climates. By conducting tests at varying temperatures, companies can optimize their product designs and material choices for durability and safety.
Advanced Humidity Control Mechanisms: Replicating Moisture Variations for Enhanced Durability Insights
Humidity is another critical factor that can drastically affect material performance. The sunshine weatherometer is equipped with sophisticated humidity control systems to simulate the effects of moisture on products. High levels of humidity can cause a range of issues, from corrosion in metals to warping in wood and degradation of adhesives.
For example, automotive manufacturers often rely on humidity testing to ensure that their vehicles' interiors, electrical systems, and exterior coatings can withstand different moisture levels, especially in tropical or coastal environments. By mimicking real-world moisture fluctuations, the weatherometer provides valuable insights into how materials will respond to condensation, dampness, or prolonged exposure to humid conditions. This allows manufacturers to refine their products for enhanced durability, helping to prevent costly failures in the field.
Integrated Environmental Simulation: Combining UV, Temperature, and Humidity for Holistic Weathering Assessments
One of the key advantages of the sunshine weatherometer is its ability to combine UV radiation, temperature, and humidity into a single, integrated test. This holistic approach provides manufacturers with a more comprehensive understanding of how their materials will perform under a variety of environmental stresses simultaneously.
For instance, a product exposed to high UV radiation, fluctuating temperatures, and moisture at the same time may degrade differently than when subjected to just one of these factors in isolation. By simulating these combined conditions, the weatherometer creates a more realistic testing environment that closely mirrors real-world scenarios. This integrated approach ensures manufacturers receive accurate data on the durability and performance of their products, allowing them to fine-tune their designs and materials for optimal longevity.
Fine-Tuning the Environment: Customizing Weatherometer Settings for Specific Testing Needs
The versatility of the sunshine weatherometer lies in its ability to be tailored to specific testing requirements. Each industry - and even each product - has unique needs when it comes to environmental stressors. Whether testing for UV degradation in outdoor signage or assessing the combined effects of temperature and humidity on electronics, the weatherometer can be fine-tuned to simulate the precise conditions a product will face in its intended environment.
This customization allows manufacturers to focus on the most relevant factors for their products, ensuring precise and accurate results. For example, a textile manufacturer may want to focus on UV and humidity exposure to assess colorfastness and fabric durability, while a solar panel manufacturer may prioritize UV exposure and temperature cycling to evaluate long-term efficiency. By fine-tuning the weatherometer's settings, manufacturers can optimize their testing processes, leading to higher-quality, more reliable products.
For more information on how LIB Industry sunshine weatherometer can help you with your environmental testing requirements, feel free to reach out at ellen@lib-industry.com.
References
1. ASTM D4329 - Standard Practice for Fluorescent UV Exposure of Plastics.
2. ISO 4892-2 - Methods of Exposure to Laboratory Light Sources, Part 2: Xenon-Arc Lamps.
3. ISO 9022-11 - Environmental Testing, Part 11: Climatic and Mechanical Stress.
4. ASTM G154 - Standard Practice for Operating Fluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Apparatus for Exposure of Nonmetallic Materials.


_1731062079549.webp)





.webq.jpg)

