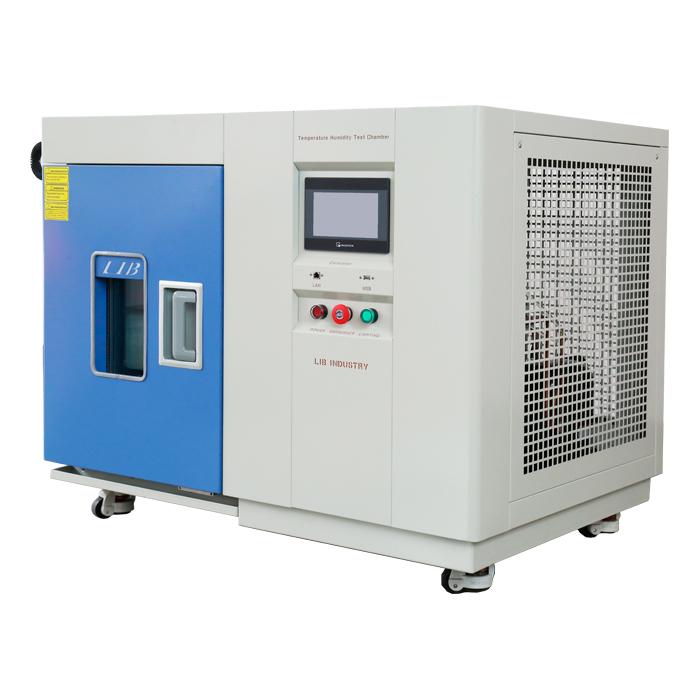
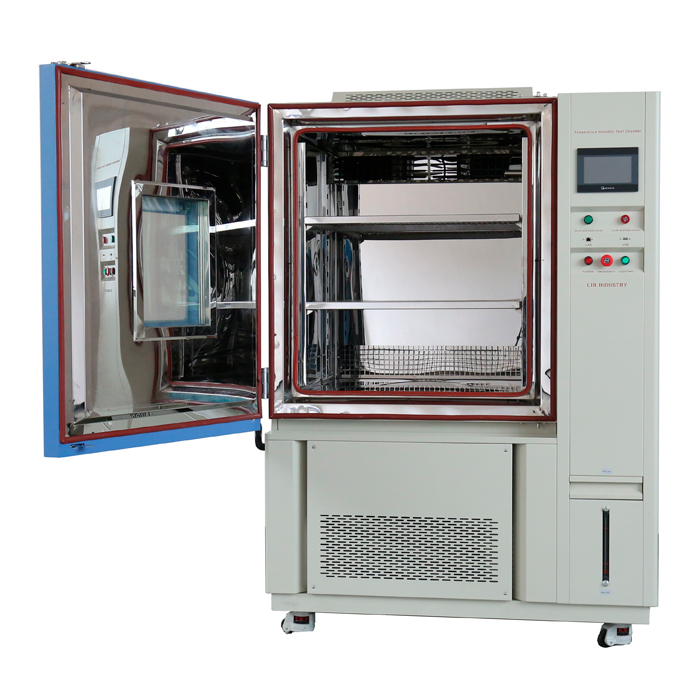
What is the standard for temperature cycling test?
Temperature cycling tests are crucial in evaluating the reliability and performance of various products under fluctuating temperature conditions. These tests simulate real-world environmental stresses that products may encounter during their lifecycle. To ensure consistency and reliability in testing procedures, industry standards have been established for temperature cycling tests. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the standards, methodologies, and importance of temperature cycling tests, with a focus on the use of temperature cycling chambers.

♦Temperature Cycling Test Standards
JEDEC Standards for Temperature Cycling
The Joint Electron Device Engineering Council (JEDEC) has established well-known standards for temperature cycling tests, especially for the electronics industry. These standards, including JESD22-A104 and JESD22-A105, offer comprehensive guidelines for performing temperature cycling on electronic components and assemblies. By specifying critical parameters such as temperature ranges, ramp rates, and dwell times, JEDEC ensures uniformity and reliability in testing practices across different facilities. These standards help manufacturers assess the durability and performance of electronic devices under varying thermal conditions, promoting quality and consistency in the production and testing processes.
IEC Standards for Environmental Testing
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed comprehensive standards for environmental testing, which include guidelines for temperature cycling tests. IEC 60068-2-14, in particular, focuses on temperature cycling for electrical and electronic equipment. This standard provides detailed procedures for subjecting products to alternating cycles of high and low temperatures, simulating real-world thermal conditions. By following these guidelines, manufacturers can evaluate their products' resilience to thermal stress, ensuring that they can maintain functionality and reliability even when exposed to extreme temperature variations. These tests are crucial for enhancing product durability and ensuring compliance with international quality standards.
MIL-STD-810 for Military and Aerospace Applications
The United States Military Standard MIL-STD-810 provides detailed specifications for environmental testing, including rigorous temperature cycling tests using a temperature cycling chamber. This standard is highly significant for products used in military and aerospace sectors, where exposure to extreme and fluctuating temperatures is a common challenge. MIL-STD-810 outlines procedures to assess the durability and performance of equipment under harsh environmental conditions, ensuring that it can withstand the stresses of rapid temperature changes. These tests are crucial for validating the robustness and reliability of military and aerospace equipment, helping ensure that it operates effectively in critical and demanding environments.
♦Key Components of Temperature Cycling Test Standards
Temperature Range and Extremes
Temperature cycling test standards typically define the temperature range and extremes to which a product should be subjected. These ranges can vary depending on the intended application and industry. For instance, consumer electronics might be tested from -40°C to +85°C, while aerospace components may undergo more extreme temperature cycles, from -65°C to +150°C or beyond. The temperature cycling chamber used must be capable of achieving and maintaining these specified temperature extremes with precision.
Ramp Rates and Transition Times
Standards often specify the rate at which temperature changes should occur during cycling tests. Ramp rates are typically expressed in degrees per minute and can significantly impact the stress experienced by the test specimen. Faster ramp rates can induce more thermal shock, while slower rates may better simulate gradual temperature changes. A well-designed temperature cycling chamber can accurately control these ramp rates, ensuring compliance with the relevant standards.
Dwell Times and Cycle Durations
Dwell times, or the duration for which a product is held at each temperature extreme, are critical parameters in temperature cycling tests. Standards may specify minimum dwell times to ensure thermal equilibrium is reached within the test specimen. The total number of cycles and overall test duration are also defined in the standards, often based on the expected lifecycle of the product or specific industry requirements.
♦Implementing Temperature Cycling Tests with Precision
Selecting the Right Temperature Cycling Chamber
Choosing an appropriate temperature cycling chamber is crucial for conducting tests that comply with industry standards. The chamber should have the capacity to achieve the required temperature range, ramp rates, and stability. Advanced temperature cycling chambers offer features like programmable controllers, real-time monitoring, and data logging capabilities, ensuring accurate and repeatable test conditions.
Test Setup and Specimen Preparation
Proper test setup is essential for obtaining reliable results. This includes careful placement of the test specimens within the temperature cycling chamber, ensuring uniform temperature distribution. Thermal sensors may be attached to critical points on the specimen to monitor actual temperature changes. The preparation of test specimens, including any pre-conditioning required by the standards, must be meticulously followed.
Monitoring and Data Analysis
Throughout the temperature cycling test, continuous monitoring of temperature profiles, humidity levels (if applicable), and specimen response is crucial. Modern temperature cycling chambers often integrate sophisticated data acquisition systems that record and analyze test parameters in real-time. Post-test analysis of this data helps in verifying compliance with the standard and identifying any anomalies or failure modes in the test specimens.
♦Conclusion
In conclusion, temperature cycling test standards provide a structured approach to evaluating product reliability under varying thermal conditions. By adhering to these standards and utilizing advanced temperature cycling chambers, manufacturers can ensure their products meet the rigorous demands of diverse operating environments. Whether you're in the electronics, automotive, or aerospace industry, understanding and implementing these standards is key to producing robust and reliable products.
If you want to learn more about this kind of Temperature Cycling Chamber, welcome to contact us info@libtestchamber.com.
References
1. JEDEC Standard JESD22-A104E, "Temperature Cycling," JEDEC Solid State Technology Association, 2014.
2. IEC 60068-2-14:2009, "Environmental testing - Part 2-14: Tests - Test N: Change of temperature," International Electrotechnical Commission, 2009.
3. MIL-STD-810H, "Environmental Engineering Considerations and Laboratory Tests," Department of Defense Test Method Standard, 2019.
4. Handbook of Environmental Degradation of Materials, Third Edition, edited by Myer Kutz, William Andrew Publishing, 2018.
5. Reliability and Failure of Electronic Materials and Devices, Second Edition, by Milton Ohring and Lucian Kasprzak, Academic Press, 2014.
6. Environmental Testing Techniques for Electronics and Materials, by Geoffrey W. A. Dummer and Norman B. Griffin, Pergamon Press, 1998.


.webp)







