What is the purpose of thermal shock?
Thermal shock testing is a critical process in the world of material science and engineering, aimed at evaluating a material or product's resistance to rapid temperature changes. This testing is essential for ensuring the reliability and durability of components exposed to extreme temperature variations in their operational environment. In this blog, we'll delve into the purpose of thermal shock testing, the standards and processes involved, and the role of thermal shock equipment manufacturers in delivering reliable testing solutions.
Understanding Thermal Shock Testing
Thermal shock testing reproduces the outrageous temperature changes that materials and items might insight in certifiable applications. The primary objective of this testing is to locate any potential flaws or failures caused by abrupt temperature changes. For example, electronic parts, aviation parts, and auto materials are frequently exposed to brutal ecological circumstances that could prompt warm shock. By presenting these things to controlled warm shock tests, makers can guarantee their items will perform dependably under such circumstances.
Thermal shock testing includes quickly cycling among high and low temperatures. If the material is not designed to withstand such conditions, this process can result in cracking, delamination, or other forms of failure. This stress is caused by the process. Engineers and designers can enhance their products' durability and dependability by using the information gleaned from these tests.
Thermal Shock Equipment: Key Features and Functions
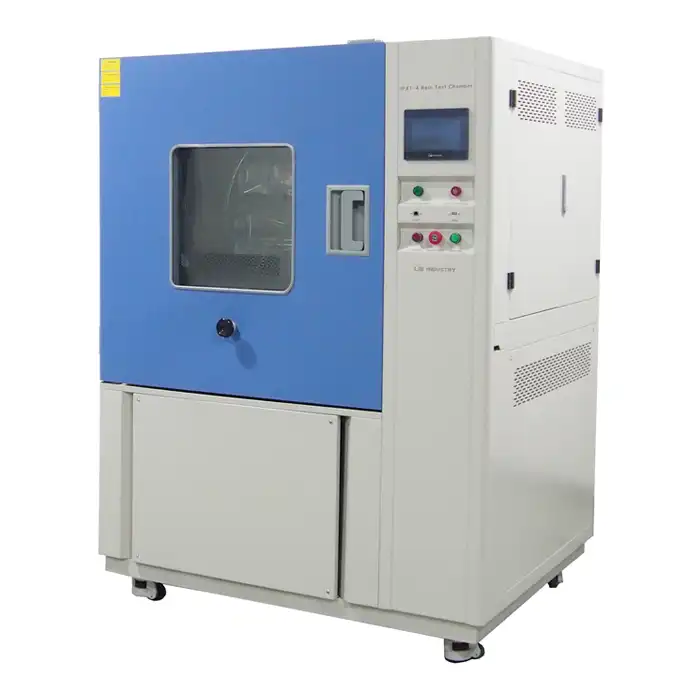
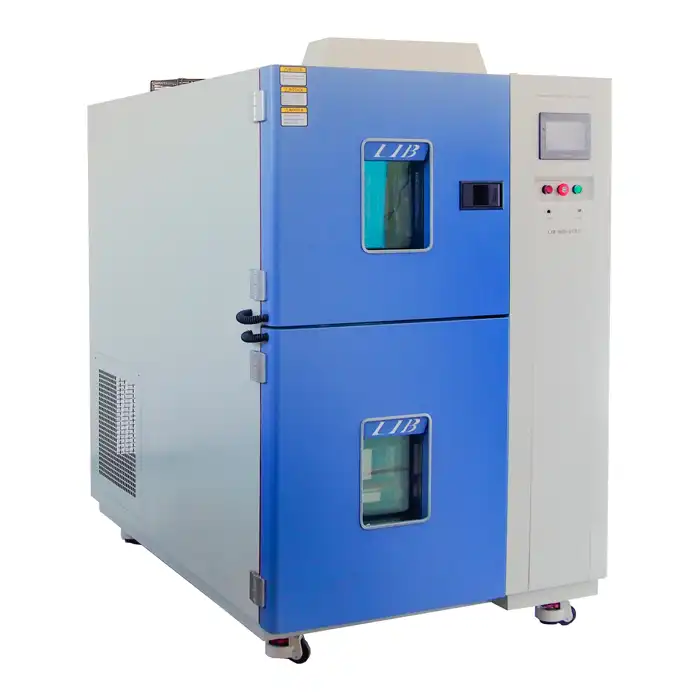
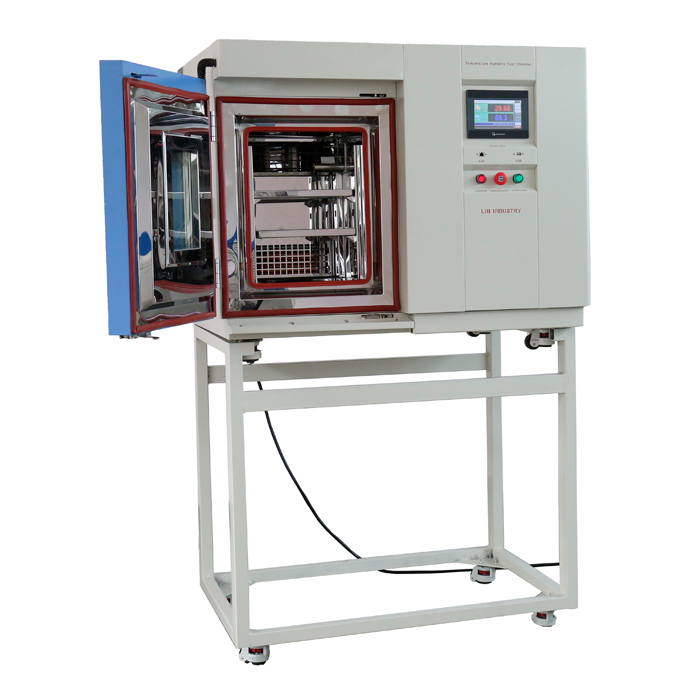
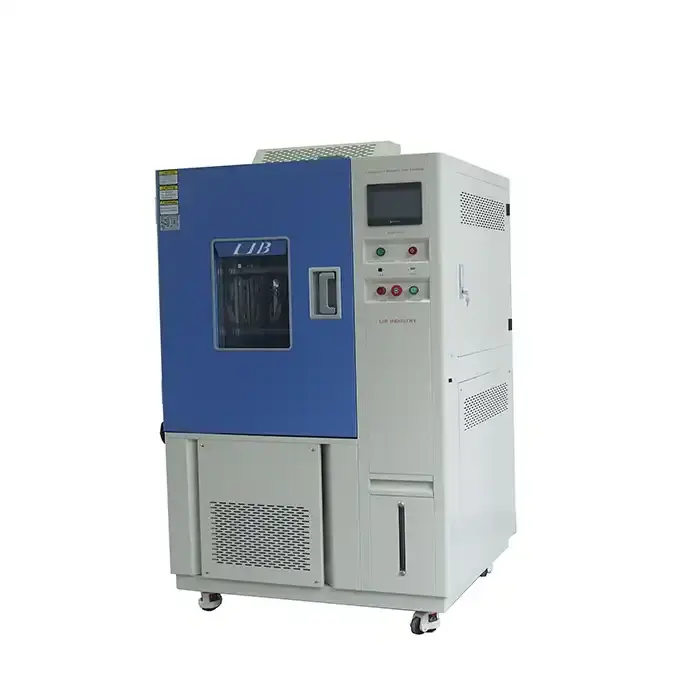
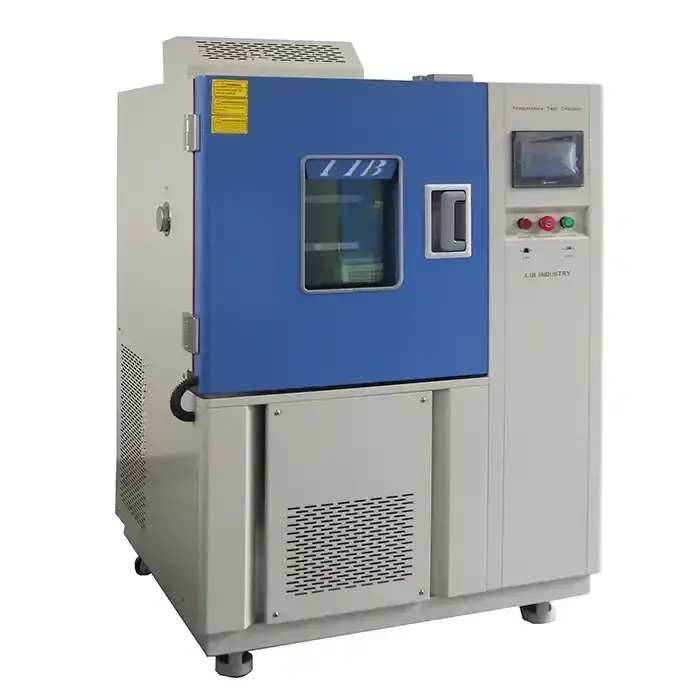
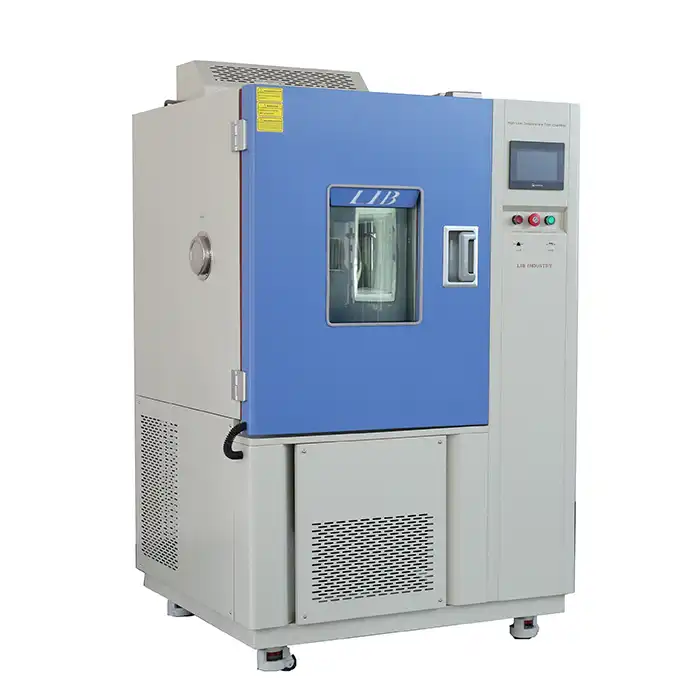
These rigorous tests require specialized thermal shock equipment. These machines have two chambers, one hot and one cold. A transfer mechanism connects them, allowing the test specimen to be quickly moved between the two environments. The material is subjected to sudden temperature changes as a result of this rapid transition, resembling actual thermal shock conditions.
Chamber Design and Temperature Range
Thermal shock equipment typically features a hot chamber capable of reaching temperatures up to 200°C (392°F) and a cold chamber that can go as low as -75°C (-103°F). This wide temperature range allows for comprehensive testing of various materials and products.
Transfer Mechanism
The transfer mechanism is crucial for the rapid movement of the test specimen between the hot and cold chambers. This mechanism must operate quickly and smoothly to ensure accurate testing results. Advanced thermal shock equipment often uses pneumatic or hydraulic systems for this purpose.
Control and Monitoring Systems
Modern thermal shock equipment is equipped with sophisticated control and monitoring systems that allow for precise regulation of temperature and transfer times. These systems ensure that the testing conditions are consistent and repeatable, providing reliable data for analysis.
Standards and Processes in Thermal Shock Testing
Thermal shock testing is governed by various industry standards that specify the testing procedures, thermal shock equipment requirements, and acceptance criteria. Some of the most widely recognized standards include:
- MIL-STD-883: This military standard outlines the methods for testing microelectronic devices, including thermal shock testing. It specifies the temperature range, dwell times, and number of cycles required to evaluate the reliability of electronic components.
- IEC 60068-2-14: The International Electrotechnical Commission standard provides guidelines for environmental testing, including thermal shock tests. It covers the procedures for subjecting specimens to sudden temperature changes and the evaluation of test results.
- ASTM D746: The American Society for Testing and Materials standard focuses on the brittleness temperature of plastics and elastomers. It includes procedures for thermal shock testing to determine the temperature at which materials become brittle and prone to failure.
The thermal shock testing process typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The test specimen is prepared and conditioned according to the relevant standards. This may involve cleaning, pre-heating, or pre-cooling the material to ensure accurate test results.
- Initial Inspection: Before testing, the specimen is inspected for any pre-existing defects or damage. This inspection provides a baseline for evaluating the effects of thermal shock.
- Testing: The specimen is subjected to a series of temperature cycles, moving rapidly between the hot and cold chambers. The number of cycles and the duration of exposure in each chamber are determined by the applicable standards.
- Post-Test Inspection: After the thermal shock testing is complete, the specimen is inspected again to identify any new defects or failures. This inspection helps assess the material's resistance to thermal shock and provides data for further analysis.
The Role of Thermal Shock Equipment Manufacturers
Thermal shock equipment manufacturers play a crucial role in providing the tools necessary for conducting reliable and accurate thermal shock tests. These manufacturers design and produce advanced testing machines that meet the stringent requirements of industry standards. Some key contributions of thermal shock equipment manufacturers include:
Innovation and Development
Leading manufacturers invest in research and development to create cutting-edge thermal shock equipment. Innovations such as improved transfer mechanisms, enhanced temperature control systems, and user-friendly interfaces contribute to more efficient and reliable testing processes.
Customization and Support
Thermal shock equipment manufacturers often offer customization options to meet the specific needs of different industries and applications. They provide support throughout the entire process, from equipment selection and installation to maintenance and calibration.
Compliance and Certification
Reputable manufacturers ensure that their equipment complies with international standards and regulations. They provide certification and documentation to demonstrate the quality and reliability of their products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, thermal shock testing is a vital process for assessing the durability and reliability of materials and products subjected to extreme temperature variations. Thermal shock equipment manufacturers play a pivotal role in delivering the advanced testing solutions needed to conduct these tests effectively. By understanding the purpose of thermal shock testing and the capabilities of modern thermal shock equipment, industries can ensure their products meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.
If you want to learn more about this kind of Thermal Shock Equipment, welcome to contact us info@libtestchamber.com.
References
1. "Department of Defense, MIL-STD-883, Test Method Standard for Microcircuits, Method 1011.9, Thermal Shock."
2. "International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC 60068-2-14: Environmental Testing - Part 2-14: Tests - Test N: Change of Temperature."
3. "ASTM International, ASTM D746-14, Standard Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastics and Elastomers by Impact."
4. "Westpak, Inc., Thermal Shock Testing Overview."
5. "D. Blom, J. P. Kelly, and P. L. Meschter, 'Environmental Stress Screening (ESS) of Electronics,' NASA Reference Publication 1392, 1996."





.webp)




