What is the purpose of the thermal shock chamber?
In the world of environmental testing, thermal shock chambers are vital tools. They are used across a variety of industries to ensure that products can withstand sudden changes in temperature without losing functionality. But what exactly is the purpose of a thermal shock chamber? In this blog post, we'll explore this question in detail, highlighting the importance of these chambers and their role in quality assurance.
What Are the Thermal Shock Chambers?
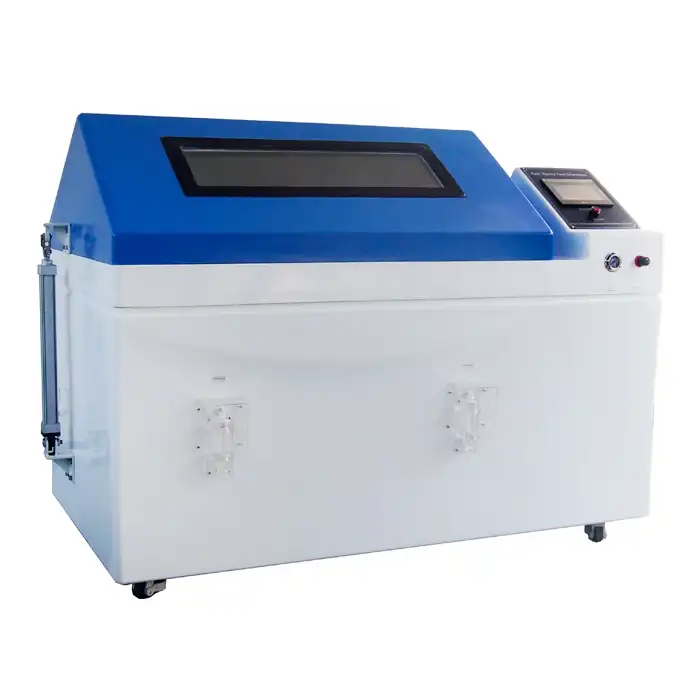
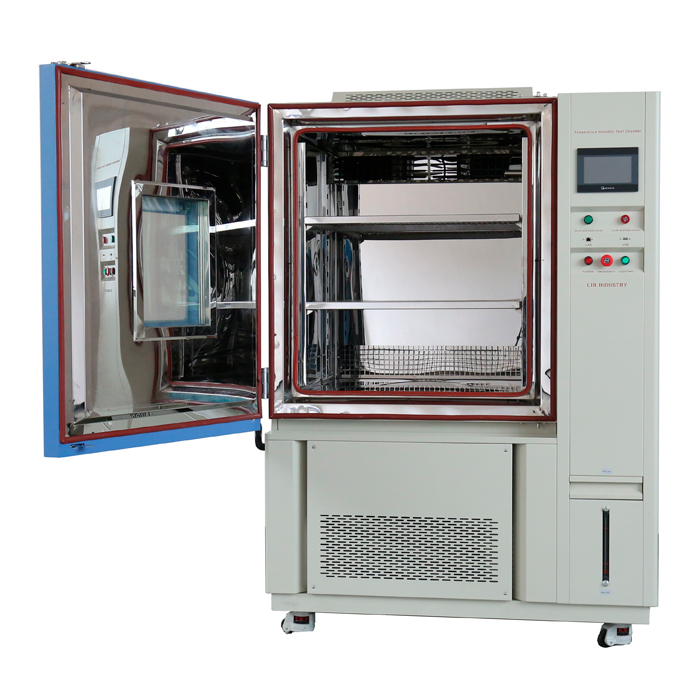
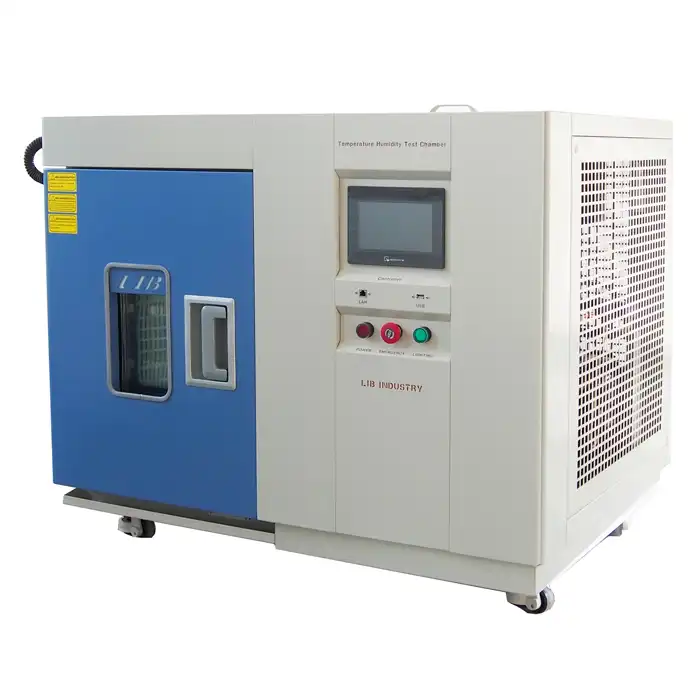
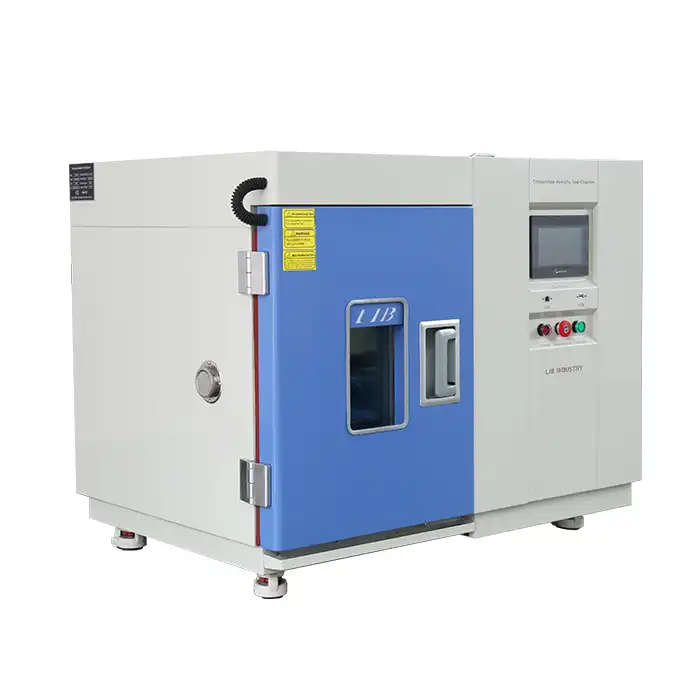
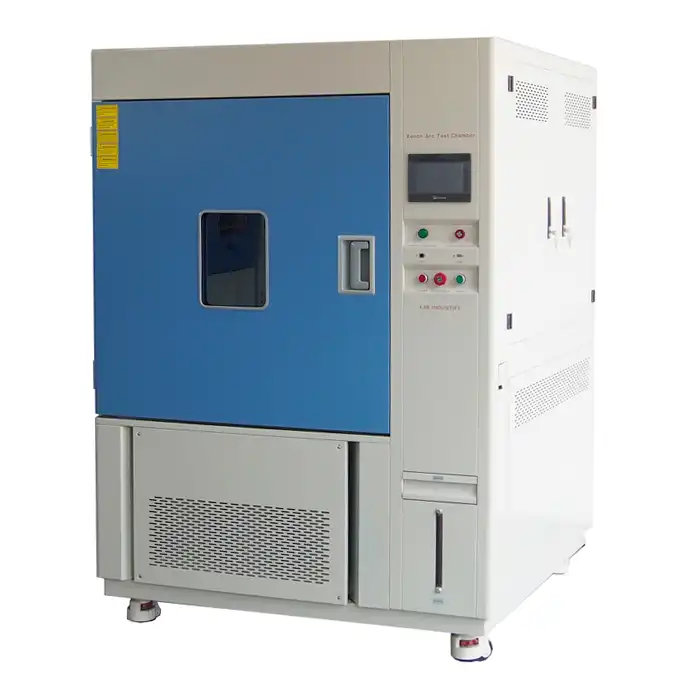
Thermal shock chambers are advanced testing devices engineered to evaluate the robustness and reliability of materials and products under extreme temperature variations. Unlike standard environmental chambers that maintain a consistent temperature, thermal shock chambers are designed to subject items to abrupt and extreme temperature changes, such as transitioning rapidly from a freezing cold environment to a scorching hot one.
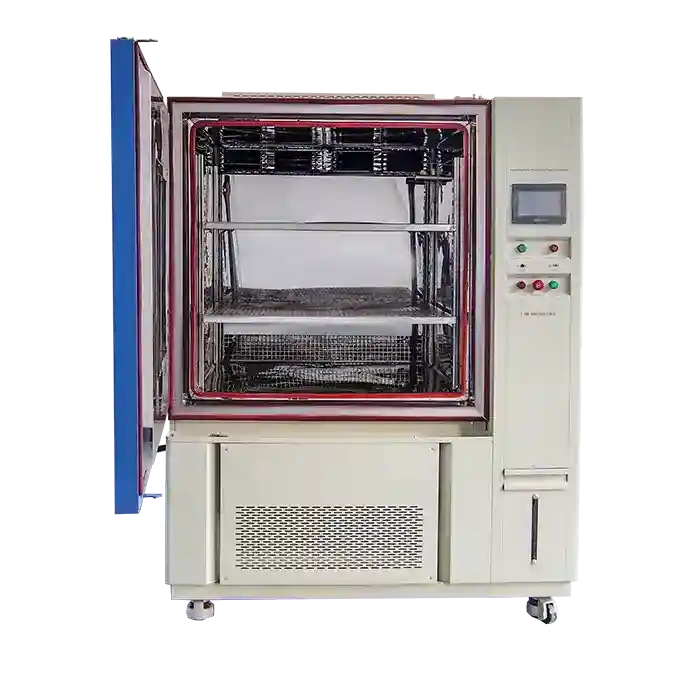
These chambers typically feature two separate sections: one for high temperatures and one for low temperatures. Thermal shock equipment manufacturers design these chambers to switch between hot and cold temperatures quickly, maintaining precise control over the testing conditions. This capability is crucial for replicating the harshest environmental conditions a product might face, ensuring comprehensive testing.
The ability to rapidly switch between hot and cold conditions allows manufacturers to observe how products react to thermal stress. This testing is crucial for identifying potential failures like thermal expansion cracks, delamination, or material degradation that might not be visible under normal temperature conditions. By using thermal shock chambers, companies can detect weaknesses before products reach the market, thereby enhancing quality assurance and reliability.
Thermal shock chambers are designed with precise control systems to ensure accurate temperature transitions and maintain testing consistency. This precision is essential for replicating real-world conditions and achieving reliable test results. In summary, thermal shock chambers are indispensable tools for manufacturers aiming to produce durable and high-performance products capable of withstanding severe environmental conditions.
What Are the Purposes of Thermal Shock Chambers?
Ensuring Product Reliability
One of the primary purposes of thermal shock chambers is to ensure the reliability of products. In industries such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace, products often encounter extreme temperature fluctuations. For instance, electronic components in a car might need to function correctly in both freezing winters and scorching summers. Thermal shock testing helps verify that these components can endure such conditions without malfunctioning.
Manufacturers rely on thermal shock equipment to simulate these environments, identifying and addressing potential points of failure. This proactive approach helps in improving product quality and reliability, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction and reduced warranty claims.
Accelerating Product Development
Thermal shock chambers also play a crucial role in accelerating product development. By exposing products to rapid temperature changes, manufacturers can quickly gather data on how their products behave under stress. This accelerated testing process allows for faster identification of design flaws and material weaknesses, enabling quicker iterations and improvements.
Thermal shock equipment manufacturers often provide customizable testing options, allowing for tailored testing protocols that meet specific industry requirements. This flexibility is essential for companies looking to innovate and bring new products to market swiftly while ensuring they meet stringent quality standards.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Many industries have strict regulations and standards regarding product durability and performance. Thermal shock testing is often a requirement to comply with these standards. For example, the automotive industry follows standards such as ISO 16750, which outlines environmental conditions and testing for electrical and electronic equipment.
Thermal shock chambers are designed to meet these regulatory requirements, providing manufacturers with the necessary tools to conduct thorough and standardized tests. By ensuring compliance, companies can avoid costly recalls, legal issues, and damage to their reputation.
How to Choose the Right Thermal Shock Equipment Manufacturer?
When selecting a thermal shock equipment factory, it's essential to consider factors such as the quality of the equipment, customization options, and customer support. Reliable manufacturers offer advanced features, such as automated testing cycles, data logging, and remote monitoring, which enhance the efficiency and accuracy of testing processes.
Moreover, partnering with a manufacturer that provides comprehensive support, including training and maintenance, ensures that the testing equipment remains in optimal condition, delivering consistent and accurate results over time. Factors to consider when selecting a thermal shock chamber manufacturer:
Equipment Quality
Look for manufacturers that use high-quality materials and components to ensure the durability and reliability of the testing chambers.
Customization Options
Different industries have unique testing requirements. Choose a manufacturer that offers customizable solutions to meet your specific needs.
Customer Support
Excellent customer support is crucial for troubleshooting, maintenance, and training. Ensure the manufacturer provides robust support services.
By carefully evaluating these factors, companies can make an informed decision and select a thermal shock equipment manufacturer that aligns with their testing needs and business objectives.
Conclusion
Thermal shock chambers are indispensable in today's competitive manufacturing landscape. They help ensure product reliability, accelerate development cycles, and comply with industry standards. By choosing the right thermal shock equipment manufacturer, companies can enhance their testing capabilities, improve product quality, and achieve greater success in their respective markets.
LIB Industry concentrates on providing the Turn-key solution for environmental testing, that research, design, producing, commissioning, delivery, install and training, provide the whole products and service according to customer's requirements. If you have any questions or need further information about Thermal Shock Chambers and their applications, feel free to contact us at info@libtestchamber.com. We are here to assist you with all your environmental testing needs.
References
1. ASTM International. (2018). ASTM D3330 / D3330M - 18 Standard Test Method for Peel Adhesion of Pressure-Sensitive Tape.
2. ISO 16750-4:2010. (2010). Road vehicles — Environmental conditions and testing for electrical and electronic equipment — Part 4: Climatic loads.
3. IEC 60068-2-14:2009. (2009). Environmental testing — Part 2-14: Tests — Test N: Change of temperature.
4. Wang, X., & Li, Y. (2017). "Thermal Shock Resistance of Ceramic Materials." Journal of Materials Science, 52(18), 109-120.
5. Montgomery, D. C. (2017). "Design and Analysis of Experiments." Wiley.
6. Simpson, W. (2019). "Thermal Cycling and Thermal Shock Testing." In Environmental Testing for Aerospace Applications, pp. 115-134. Springer.
7. Murray, J. J. (2016). "Thermal Shock Chambers: Technology and Application." Industrial Testing Equipment Review, 23(4), 45-52.






.webp)



