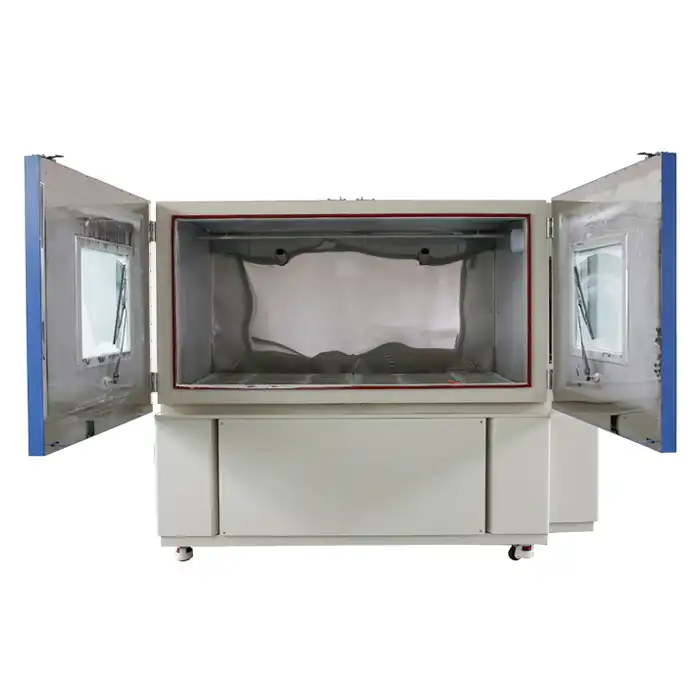
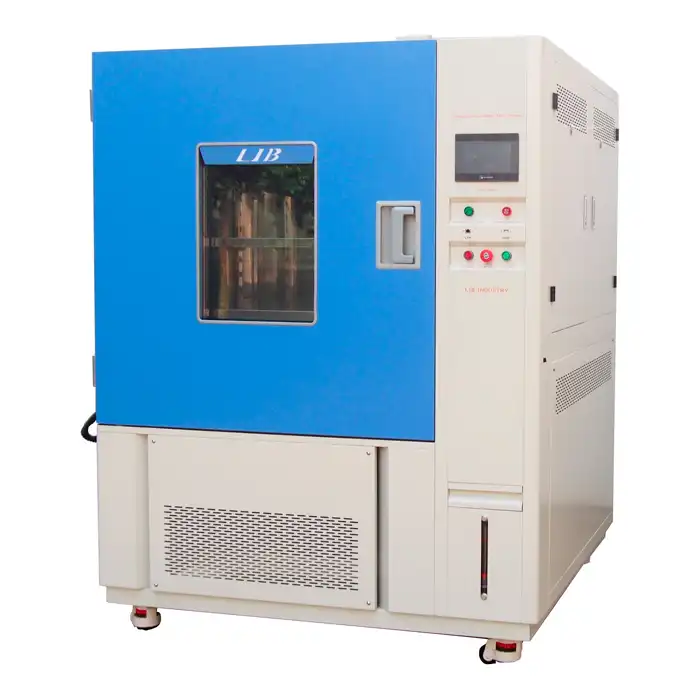
What is a thermal cycling chamber?
In the realm of environmental testing, understanding how products withstand temperature fluctuations is crucial. One of the key tools used for this purpose is the thermal cycling chamber. This device is designed to simulate various temperature conditions to test the durability and reliability of materials and products. Whether you’re involved in manufacturing, electronics, or any other field where temperature stability is vital, knowing how a thermal cycling chamber operates, and its importance can be incredibly beneficial.
How Does a Thermal Cycling Chamber Work?
A thermal cycling chamber is an advanced testing device engineered to evaluate how materials and components perform under extreme temperature conditions. It simulates the rapid temperature changes that products may experience in real-world scenarios, helping to assess their durability and reliability. Here’s a detailed look at how a thermal cycling chamber operates:
Temperature Variation
The core function of a thermal cycling chamber is to create and control temperature variations. This is achieved through the chamber's ability to rapidly switch between high and low temperatures. The process generally involves:
- Heating and Cooling Systems: The chamber is equipped with precise heating and cooling mechanisms, such as electric heaters and refrigeration units. These systems work together to achieve the desired temperature extremes.
- Customizable Cycles: The temperature changes can be programmed according to the specific testing requirements. For example, a chamber can be set to alternate between high temperatures of 100°C and low temperatures of -40°C, depending on what is being tested.
- Temperature Ramp Rates: The speed at which the temperature changes (ramp rate) can be adjusted to simulate different conditions. Faster ramp rates can be used to test products that are exposed to rapid temperature changes, while slower rates are used for more gradual transitions.
These temperature variations are crucial for simulating the thermal stresses that materials and components may encounter during their lifecycle, such as those experienced in automotive engines, electronics, or aerospace components.
Controlled Environment
Maintaining a controlled environment is essential for accurate and consistent testing. Here’s how the thermal cycling chamber ensures a stable testing environment:
- Precision Temperature Control: The chamber’s temperature control system ensures that the environment inside the chamber remains at the set temperature. This precision is critical for obtaining reliable test results and avoiding any inconsistencies.
- Humidity Control: In addition to temperature, some chambers also regulate humidity levels. This is important for testing materials that may be sensitive to moisture or require specific humidity conditions to accurately simulate real-world scenarios.
- Stable Conditions: The chamber is designed to minimize external influences that could affect the testing conditions. This includes insulation to prevent heat loss or gain and ensuring that the chamber’s internal environment remains stable throughout the test.
Test Execution
The execution of tests within a thermal cycling chamber involves several key steps:
- Sample Placement: Products or materials are carefully placed inside the chamber. The placement is often done in a manner that ensures even exposure to the temperature changes, which can include using racks or holders designed to maximize test accuracy.
- Test Protocols: The thermal cycling chamber can be programmed to follow specific test protocols, which dictate the temperature cycles, duration, and frequency of temperature changes. These protocols are tailored to match the requirements of the product being tested.
- Monitoring and Control: During the test, the chamber continuously monitors the temperature and adjusts as needed to maintain the set conditions. The chamber’s control system ensures that any deviations from the desired temperature range are promptly corrected.
Data Collection
Data collection is a vital aspect of the thermal cycling process. Here’s how the chamber facilitates this:
- Instrumentation: The chamber is equipped with various sensors and instruments to measure key parameters such as temperature fluctuations, material deformation, and performance metrics.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Data is collected in real-time and can be monitored through a control panel or software interface. This allows for immediate analysis and ensures that any issues can be addressed promptly.
- Post-Test Analysis: After the test is complete, the collected data is analyzed to evaluate the performance of the material or product. This analysis helps in understanding how the item responds to thermal stress and provides insights into its durability and potential areas for improvement.
Why is Thermal Cycling Important?
Thermal cycling tests are essential for several reasons:
Product Reliability
Testing products under thermal cycling conditions ensures that they can withstand the temperature variations they might encounter during their lifecycle. This is particularly important for electronics, automotive parts, and other components exposed to fluctuating temperatures.
Quality Assurance
By simulating real-world conditions, thermal cycling chambers help in identifying potential weaknesses in materials or products before they reach the market. This proactive approach to quality control can prevent costly failures and enhance product reliability.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries have specific standards and regulations regarding temperature performance. Thermal cycling tests help ensure that products meet these standards, facilitating compliance with industry requirements and enhancing customer trust.
Improved Design
The data obtained from thermal cycling tests can be used to improve product design. Engineers and designers can use this information to make modifications that enhance durability and performance, leading to better and more reliable products.
How to Choose the Right Thermal Cycling Chamber?
There are several factors to consider when buying thermal cycling chambers:
Temperature Range
Ensure that the chamber can achieve the required temperature extremes for your testing needs. Different applications might require different temperature ranges, so it’s important to choose a chamber that meets your specific requirements.
Chamber Size
Depending on the size of the items being tested, you’ll need to choose a chamber with adequate space. Smaller chambers are suitable for individual components, while larger chambers are necessary for bulkier items.
Control Precision
The accuracy and stability of temperature control are crucial for reliable testing. Look for chambers with precise temperature control to ensure consistent and accurate test results.
Data Acquisition
Advanced thermal cycling chambers come with data acquisition systems that allow for detailed monitoring and analysis of test results. This feature can be valuable for comprehensive testing and analysis.
Ease of Use
Consider user-friendly interfaces and automation features that can simplify the testing process and improve efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a thermal cycling chamber is a vital tool for testing and ensuring the durability of materials and products under varying temperature conditions. By understanding its operation and significance, you can better appreciate its role in maintaining product reliability and quality.
If you need more information about thermal cycling chambers or are looking for a solution tailored to your needs, feel free to contact us at info@libtestchamber.com.
References
1. "Thermal Cycling Chamber Testing: Best Practices and Benefits". ASTM International.
2. "Understanding Thermal Cycling Chambers and Their Applications". Environmental Test Equipment.
3. "Thermal Cycling Chambers: Operation and Applications in Reliability Testing". TechBriefs.
4. "A Comprehensive Guide to Thermal Cycling Testing for Electronics". Electronic Design.
5. "Selecting the Right Thermal Cycling Chamber: Key Considerations". Lab Manager.