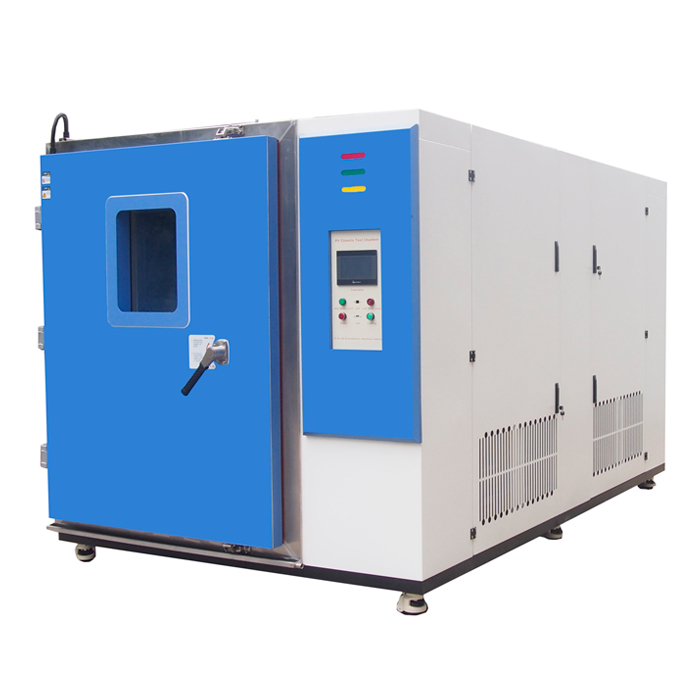
How does an UV chamber work?
Understanding how a UV test chamber works is essential for industries that need to ensure the durability and reliability of their products when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. UV test chambers simulate the effects of sunlight, enabling manufacturers to predict how their products will withstand long-term exposure. This article will delve into the working principles of UV test chambers, the standards they adhere to, and the testing processes involved.
What Are the Key Components of a UV Test Chamber?
UV test chambers are sophisticated devices designed to replicate the damaging effects of UV light on materials. To understand how they work, it is essential to know their main components:
UV Light Source
The primary component of a UV test chamber is the UV light source. This can be either fluorescent UV lamps or xenon arc lamps. Fluorescent UV lamps are commonly used because they offer a consistent spectrum of UV light. Xenon arc lamps, on the other hand, mimic the full spectrum of sunlight, including UV, visible, and infrared light.
Test Chamber
This is the enclosed space where the test samples are placed. It is designed to ensure that the UV light uniformly reaches all samples. The chamber is usually equipped with temperature and humidity controls to simulate various environmental conditions.
Control System
Modern UV test chambers come with sophisticated control systems that allow precise regulation of light intensity, temperature, and humidity. These systems can also program different test cycles to replicate various environmental conditions over time.
Sample Holders
These are used to secure the test samples within the chamber. They ensure that samples are exposed to UV light at the correct angles and distances, ensuring consistent and reliable results.
By understanding these components, we can appreciate how a UV test chamber creates controlled conditions to test the durability and resilience of materials.
What Testing Standards Do UV Chambers Follow?
For UV test chambers to provide reliable and comparable results, they must adhere to specific testing standards. These standards ensure that tests are performed consistently and that the results are meaningful across different industries and applications. Some of the key standards include:
ASTM G154
This is one of the most widely used standards for UV exposure testing. It provides guidelines for using fluorescent UV lamps to simulate the effects of sunlight on materials. The standard specifies test conditions, including the type of UV lamps to be used, the duration of exposure, and the temperature and humidity levels.
ISO 4892-3
This international standard outlines the methods for exposing materials to UV light using fluorescent UV lamps. It includes detailed procedures for preparing test samples, conducting the test, and evaluating the results.
ASTM G155
This standard is similar to ASTM G154 but uses xenon arc lamps instead of fluorescent UV lamps. It provides guidelines for simulating full-spectrum sunlight, making it suitable for testing materials that will be exposed to outdoor conditions.
ISO 11341
This standard specifies methods for exposing coatings to artificial weathering using UV light and water. It is particularly relevant for industries that need to test the durability of coatings and finishes.
By adhering to these standards, UV test chambers ensure that the tests are conducted consistently and that the results are reliable and comparable across different laboratories and industries.
How Are UV Tests Conducted in a UV Chamber?
The process of conducting UV tests in a UV chamber involves several steps to ensure accurate and reliable results. Here’s a step-by-step overview of the testing process:
Sample Preparation
The first step is to prepare the test samples. This involves cleaning the samples to remove any contaminants that could affect the results. Samples are then mounted on the sample holders, ensuring they are positioned correctly for uniform exposure to UV light.
Setting Test Parameters
The next step is to set the test parameters according to the relevant standards. This includes selecting the type of UV lamp, setting the light intensity, temperature, and humidity levels, and programming the test cycle. The control system of the UV chamber allows precise regulation of these parameters.
Conducting the Test
Once the test parameters are set, the UV chamber is activated, and the samples are exposed to UV light for a specified duration. The duration of the test can vary depending on the material being tested and the desired outcome. Some tests may run for several hours, while others may last for weeks or even months.
Monitoring and Recording
During the test, the UV test chamber’s control system continuously monitors and records the test conditions. This data is essential for ensuring that the test is conducted consistently and for analyzing the results.
Evaluation of Results
After the test is complete, the samples are removed from the chamber and evaluated. This may involve visual inspection, measuring changes in physical properties, or conducting further tests to assess the material’s durability. The results are compared to the pre-test condition to determine the effects of UV exposure.
Reporting
Finally, a detailed report is prepared, documenting the test conditions, procedures, and results. This report is essential for manufacturers to understand the UV resistance of their materials and to make informed decisions about product development and improvement.
Conclusion
UV test chambers play a crucial role in ensuring that materials can withstand the damaging effects of UV light. By understanding the key components, adhering to established standards, and following precise testing procedures, and purchasing and using the product through a reliable UV test chamber manufacturer, industries can ensure their products' durability and reliability.
If you want to learn more about this kind of UV Test Chamber, welcome to contact us info@libtestchamber.com.
References
1. ASTM G154-16: Standard Practice for Operating Fluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Apparatus for Exposure of Nonmetallic Materials
2. ISO 4892-3:2016: Plastics — Methods of exposure to laboratory light sources — Part 3: Fluorescent UV lamps
3. ASTM G155-13: Standard Practice for Operating Xenon Arc Light Apparatus for Exposure of Non-Metallic Materials
4. ISO 11341:2004: Paints and varnishes — Artificial weathering and exposure to artificial radiation — Exposure to filtered xenon-arc radiation
5. Atlas Material Testing Technology: UV Test Chambers.
6. Q-Lab Corporation: Understanding UV Light Exposure Testing.






.webp)



