The Importance of Xenon Weathering Tests for Paints and Coatings
Ensuring the long-term durability of paints and coatings is a critical concern for manufacturers across industries. Xenon weatherometer play a pivotal role in evaluating how coatings withstand exposure to environmental elements.

Why Weathering Resistance Matters for Paints and Coatings?
Weathering resistance is crucial for maintaining the aesthetic and protective qualities of paints and coatings over time. Exposure to sunlight, humidity, temperature fluctuations, and pollutants can degrade coatings, causing fading, cracking, and peeling. These issues affect not only the appearance but also the functionality of coatings, potentially compromising the surfaces they are meant to protect. Manufacturers who invest in high-performance coatings can ensure product longevity, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance customer satisfaction by testing for weathering resistance.
How Xenon Arc Testing Simulates Real-World Exposure Conditions?
Xenon arc testing, performed using a xenon weatherometer, replicates the full spectrum of natural sunlight, including ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared light, to simulate real-world weathering conditions. This method is essential for understanding how coatings will perform under long-term environmental stress. The xenon arc produces a broad wavelength range that mimics sunlight, ensuring that testing captures the most damaging effects of UV radiation, heat, and moisture.
For example, a 2000-hour accelerated test cycle in a xenon weatherometer can simulate years of outdoor exposure, providing valuable data on a coating's durability in a fraction of the time. By adjusting parameters like humidity, temperature, and light intensity, manufacturers can simulate a variety of climates and environments, from tropical to desert conditions. This flexibility allows for comprehensive testing, ensuring that coatings will perform consistently, whether in extreme heat, high humidity, or intense sunlight.
Key Performance Factors Evaluated in Xenon Weathering Tests
Xenon weathering tests assess a range of performance factors that are critical to the longevity and effectiveness of paints and coatings:
- Color retention: Over time, exposure to UV light can cause colors to fade. Xenon weathering tests measure color changes, ensuring that coatings maintain their appearance throughout their lifespan.
- Gloss retention: High-gloss coatings are often prized for their appearance, but they can become dull under prolonged exposure to sunlight and environmental pollutants. Testing for gloss retention ensures that surfaces remain visually appealing.
- Cracking and peeling resistance: Extreme temperature fluctuations and UV exposure can cause coatings to crack or peel, compromising the protective layer. Xenon weathering helps identify formulations that resist these issues.
- Chalking resistance: Outdoor exposure can lead to the formation of a powdery residue, known as chalking, on the surface of coatings. Testing for chalking resistance ensures that coatings maintain a smooth and clean finish.
Data from xenon weathering tests conducted using a xenon weatherometer provide manufacturers with concrete insights into how their coatings will perform over time. This enables them to optimize formulations and ensure their products offer superior protection and durability.
Best Practices for Conducting Accurate Xenon Weathering Tests on Coatings
To obtain the most reliable and actionable results from xenon weathering tests, it's crucial to follow best practices in test setup and execution:
- Sample preparation: Properly preparing test samples is essential for accurate results. Surfaces should be clean, free of contaminants, and applied according to the manufacturer's specifications to avoid skewed outcomes.
- Realistic test cycles: While xenon weathering tests are accelerated, they should still mimic the specific environmental conditions the coating will experience. For example, coatings destined for tropical climates should undergo high-humidity and intense UV cycles, while those for colder regions may require freeze-thaw cycles.
- Regular monitoring: Throughout the testing process, samples should be regularly monitored and evaluated for visual changes such as fading, cracking, or chalking. This allows manufacturers to adjust formulations or application methods as needed.
- Post-test analysis: After testing, samples should be thoroughly analyzed using both visual inspection and quantitative measurements, such as spectrophotometers for color change or gloss meters to assess surface sheen. This data drives improvements in product performance.
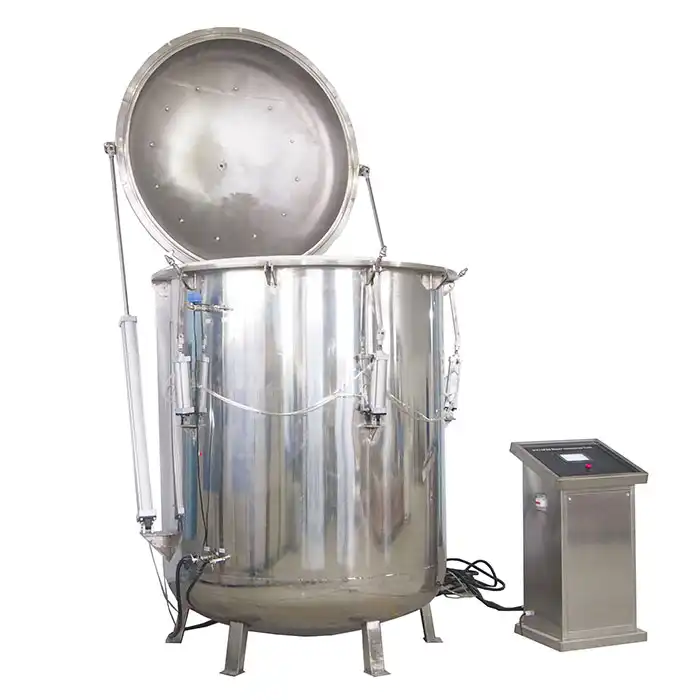
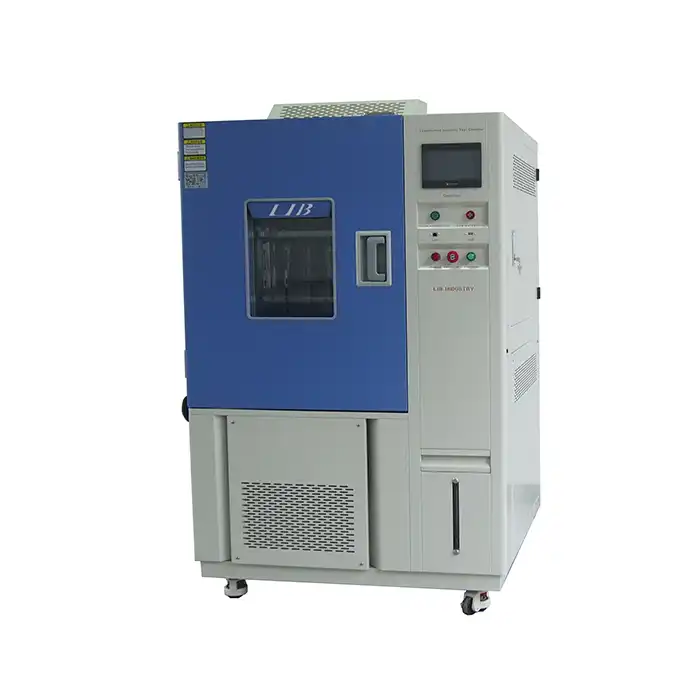
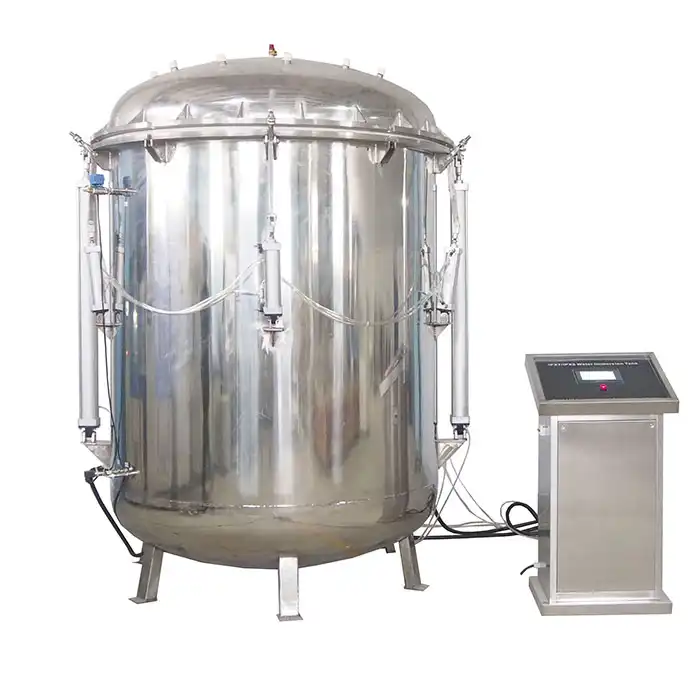
LIB Xenon Weatherometer
LIB Industry offers a state-of-the-art xenon weatherometer, designed to provide precise and reliable results for manufacturers in need of accelerated weathering tests. Key features include:
- Full-spectrum xenon arc lamp: Mimics natural sunlight, including UV, visible, and infrared light, allowing for comprehensive testing of coatings under realistic conditions.
- Customizable test parameters: Users can adjust humidity, temperature, and light intensity to simulate various environmental conditions, ensuring tests are tailored to specific product requirements.
- Durable, user-friendly design: LIB's xenon weatherometer is built for long-term use, featuring intuitive controls and high-quality materials, making it easy to operate and maintain.
- Data accuracy and reliability: The advanced sensors and controls ensure precise environmental simulations, providing accurate data that helps manufacturers optimize their coatings for durability and performance.
LIB Industry is dedicated to helping manufacturers improve their products through comprehensive testing solutions. For more information or inquiries about our xenon weatherometer, contact us at ellen@lib-industry.com.
References
1. ASTM International. (2020). Standard Practice for Operating Xenon Arc Light Apparatus for Exposure of Non-Metallic Materials.
2. ISO. (2021). Paints and Varnishes: Methods of Exposure to Laboratory Light Sources - Xenon-Arc Lamps.
3. Ghosh, S. K. (2018). Functional Coatings: Principles, Techniques, and Applications. John Wiley & Sons.
4. Holik, H. (2016). Coatings Technology Handbook. CRC Press.