What is the difference between salt spray and salt fog?
Introduction
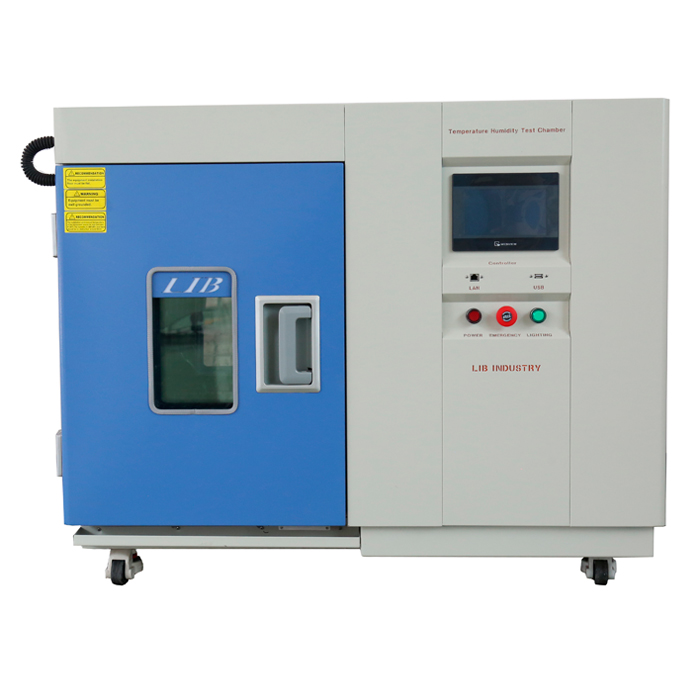
In the world of corrosion testing, two terms often come up: salt spray and salt fog. While they might sound similar, they refer to different testing methods used to evaluate the corrosion resistance of materials. Understanding the difference between these two methods is crucial for industries that rely on materials that must withstand harsh environments. A salt spray cabinet, otherwise called a salt splash chamber, is a specific testing contraption used to reproduce and assess the consumption obstruction of materials and coatings under controlled natural circumstances. In industries like automotive, aerospace, marine, and manufacturing, where exposure to corrosive environments like saltwater or road salts is a concern, this equipment plays a crucial role.In this article, we will delve into the specifics of salt spray and salt fog testing, their differences, and how they are used in industry.
What is Salt Spray Testing?
Salt spray testing, also known as salt corrosion testing, is a method used to evaluate the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings when exposed to a saline environment. This process is widely used across industries to assess the durability of materials under harsh conditions, particularly in marine and automotive sectors.
Purpose and Methodology: Salt spray tests simulate the corrosive conditions that materials may encounter in real-world environments, such as coastal areas or where road salt is used. By subjecting samples to a controlled saline mist in a chamber, testers can accelerate corrosion processes and assess how quickly materials degrade.
Industry Standards: Various standards govern salt spray testing, including ASTM B117 and ISO 9227. These standards specify test parameters such as duration of exposure, concentration of salt solution, and evaluation criteria for corrosion products.
Types of Materials Tested: Automotive components, marine equipment, industrial coatings, and aerospace parts are common subjects for salt spray testing. It helps manufacturers ensure that their products can withstand prolonged exposure to corrosive environments without significant degradation.
Evaluation Criteria: Test results are evaluated based on visual inspection of corrosion patterns, such as blistering, rust formation, or changes in appearance. Longer resistance to corrosion indicates higher durability and suitability for specific applications.
Limitations and Considerations: While salt spray testing provides valuable insights into material performance, it may not perfectly replicate all aspects of natural corrosion processes. Therefore, results should be interpreted alongside other durability tests and field performance data.
Advancements and Alternatives: Some industries have developed alternative test methods or enhanced salt spray tests with additional parameters to better reflect actual environmental conditions and improve testing accuracy.
Overall, salt spray testing plays a crucial role in quality assurance and product development by helping manufacturers identify materials and coatings that offer superior corrosion resistance, thereby enhancing the longevity and reliability of their products in challenging environments.
What is Salt Fog Testing?
Salt fog testing is a standardized method used to evaluate the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings when exposed to a saline environment. This process is essential across various industries to assess how well materials can withstand corrosion under harsh conditions, such as marine or automotive environments.A salt fog cabinet is a testing device designed to evaluate the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings under controlled conditions.
Purpose and Methodology: Salt fog testing involves placing test specimens in a controlled chamber where they are exposed to a dense fog of saline solution. This environment accelerates the corrosion process, allowing testers to observe and evaluate the effects over a relatively short period compared to natural exposure.
Industry Applications: It is widely employed in industries like automotive manufacturing, aerospace, marine equipment, and electronics, where materials need to withstand corrosive conditions. Manufacturers use salt fog testing to ensure their products meet durability standards and regulatory requirements.
Standards and Procedures: The testing procedure follows standards set by organizations such as ASTM International (ASTM B117) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO 9227). These standards define parameters like solution concentration, exposure duration, and evaluation criteria for corrosion effects.
Evaluation Criteria: During testing, technicians assess the extent of corrosion on specimens based on visual inspection criteria such as rust formation, blistering, or changes in appearance. Results help determine the material's suitability for specific applications and environments.
Limitations and Considerations: While salt fog testing provides valuable insights into material performance under controlled conditions, it may not fully replicate all aspects of real-world corrosion processes. Therefore, results should be interpreted alongside other durability tests and field performance data.
Advancements and Alternatives: Continuous research aims to improve testing accuracy and relevance. Some industries explore alternative methods or enhanced testing protocols that better simulate actual environmental conditions, ensuring more accurate predictions of material longevity.
In conclusion, salt fog testing remains a fundamental tool in quality assurance and product development, enabling manufacturers to produce materials and coatings that offer superior corrosion resistance and durability. By simulating aggressive environmental conditions in a controlled setting, this testing method helps ensure the reliability and longevity of products in challenging operational environments.
What is Their Differences in Application?
Salt spray testing and salt fog testing are both methods used to evaluate the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings, but they differ in their specific applications and testing environments.
Salt Spray Testing:
Methodology: Salt spray testing, governed by standards like ASTM B117 and ISO 9227, involves exposing test specimens to a continuous, atomized spray of salt solution.
Environment: The test chamber generates a fog-like mist of salt solution at a specified concentration (typically 5% sodium chloride) and operates continuously.
Purpose: It is used to simulate the effects of saltwater exposure on materials, making it particularly relevant for marine applications and automotive components subjected to road salts.Salt spray cabinet is used to evaluate a wide range of materials, including metals, alloys, plastics, and coatings.
Salt Fog Testing:
Methodology: Salt fog testing is similar but involves intermittently spraying a salt solution into the chamber, creating cycles of wet and dry conditions.
Environment: The intermittent spraying mimics real-world conditions where materials are exposed to alternating periods of moisture and dryness, which can affect corrosion differently.
Purpose: This method is often used to evaluate how materials withstand cyclic corrosion conditions, such as those found in outdoor environments where humidity levels fluctuate.
Applications:
Salt Spray Testing: Commonly applied in industries requiring continuous exposure simulations, such as automotive manufacturing (for assessing durability against road salt) and marine equipment (to test resistance against saltwater corrosion).
Salt Fog Testing: More suitable for applications where materials are exposed to cyclic wet and dry conditions, such as outdoor structures, electronic components, and aerospace parts subjected to varying humidity levels.Salt fog climate chamber is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and marine to ensure products meet corrosion resistance standards and to guide material selection and coating development.
Evaluation and Standards:
Both methods follow specific standards for test conditions, exposure durations, and evaluation criteria for corrosion effects.
Results from these tests help manufacturers determine the suitability of materials and coatings for their intended environments, ensuring they meet durability and performance requirements.
While salt spray testing provides a constant exposure environment, salt fog testing offers insights into how materials respond to fluctuations in moisture and dryness, which can be critical for outdoor applications.
Choosing between these methods depends on the specific environmental conditions materials will face in their intended use, guiding manufacturers in selecting the most appropriate testing protocol.
In summary, while both salt spray testing and salt fog testing serve to evaluate corrosion resistance, their distinct methodologies and applications cater to different environmental conditions and industry requirements. Manufacturers utilize these tests to ensure their products meet performance standards and can withstand the corrosive challenges of their operational environments effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, although salt fog and salt spray testing are both utilized to assess a material's resistance to corrosion, their methods of creating the corrosive environment and the severity of the test conditions are distinct. Understanding these distinctions is fundamental for ventures that depend on materials that should endure erosion, assisting them with picking the most proper testing strategy for their particular necessities. Salt spray cabinets are indispensable tools for assessing and improving the durability of materials against corrosion.These tests are used by manufacturers to ensure that their products can effectively withstand the corrosive challenges of their operational environments and meet performance standards.
For more information about salt spray and salt fog testing, please contact us at 8888.
References
ASTM B117 - Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus.
ISO 9227:2017 - Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres - Salt spray tests.
"Comparison of Salt Spray, Prohesion, and Cyclic Corrosion Testing" by C. Leyland and A. J. McPhail.
"Evaluation of protective coatings by salt spray and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy" by M. F. Montemor et al.
"Corrosion Behavior of Automotive Coatings: Salt Spray vs. Cyclic Corrosion Test" by M. Kutz et al.