What is the difference between salt fog and salt spray test?
In the realm of environmental testing, the terms "salt fog" and "salt spray" are often used interchangeably. However, they refer to distinct testing methods that serve unique purposes. For industries that rely on the durability and corrosion resistance of materials, understanding these differences is crucial. This blog aims to clarify the distinctions between salt fog and salt spray tests, providing valuable insights for manufacturers and suppliers alike. If you are in the market for reliable salt fog test cabinet suppliers, this guide will also help you make an informed decision.
What Is Salt Fog Testing?
Salt fog testing, also known as salt mist testing, is a widely used method to simulate and accelerate corrosion processes. This test involves exposing materials to a controlled salt-laden environment to evaluate their corrosion resistance. Here’s a detailed look at what salt fog testing entails:
Procedure and Purpose
The salt fog testing procedure involves placing test specimens inside a specialized chamber where they are exposed to a fine mist of salt solution, commonly sodium chloride (NaCl). The testing chamber is meticulously controlled to maintain specific temperature and humidity conditions, typically around 35°C (95°F) and 95% relative humidity.
The primary purpose of salt fog testing is to evaluate the durability and resistance of materials and coatings to corrosion. By accelerating the corrosion process, the test helps identify potential vulnerabilities in coatings, paints, and metal finishes before they are exposed to actual environmental conditions.
Applications and Benefits
Salt fog testing is extensively used across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and marine sectors, where materials are frequently exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Similarly, in the aerospace industry, this testing ensures that components can withstand the corrosive effects of atmospheric conditions at high altitudes. In the marine sector, where materials are constantly exposed to saltwater, salt fog testing helps in evaluating the effectiveness of protective coatings.
The benefits of salt fog testing extend beyond simply identifying corrosion issues. It provides valuable insights into the performance and longevity of materials and coatings, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions about material selection and protective measures. By addressing potential corrosion issues early in the design and manufacturing process, companies can enhance product reliability, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall product quality.
Key Considerations
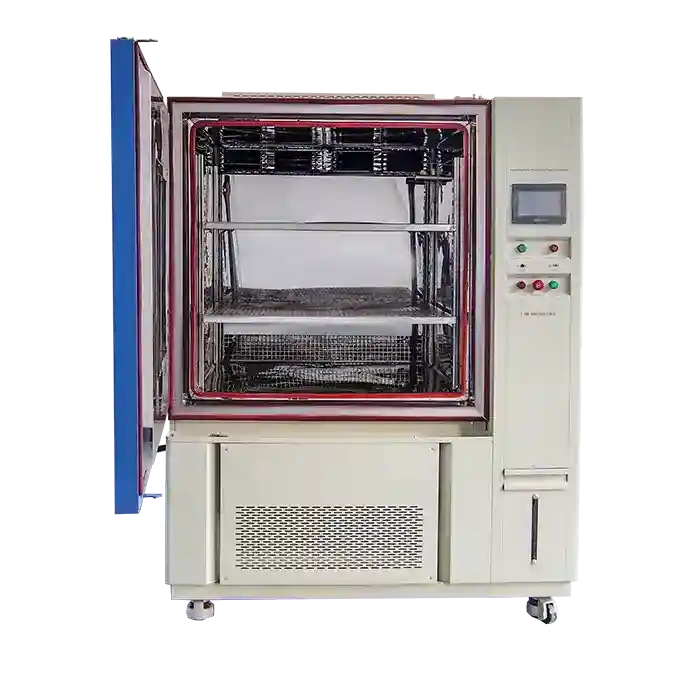
When selecting a salt fog test cabinet, it is essential to consider several factors to ensure accurate and reliable testing results. Key considerations include:
- Chamber Size: The size of the test chamber should accommodate the dimensions of the test specimens and allow for proper airflow and mist distribution.
- Control Accuracy: High-quality cabinets should offer precise control over temperature, humidity, and salt mist concentration to ensure consistent testing conditions.
- Ease of Maintenance: The construction materials of the chamber should be resistant to corrosion themselves, and the design should facilitate easy cleaning and maintenance to prevent contamination and ensure accurate results.
What Is Salt Spray Testing?
Salt spray testing, while similar in name, differs significantly in methodology and application. This section delves into the specifics of salt spray testing, highlighting its unique aspects.
Procedure and Setup
Salt spray testing involves the continuous application of a fine mist of salt solution onto test specimens. The testing chamber is designed to create a controlled environment where a salt solution, typically consisting of 5% sodium chloride (NaCl), is sprayed onto the specimens. The salt solution is atomized to form a fine mist that is consistently applied at a controlled rate, ensuring a uniform distribution across the test surfaces.
The standard temperature for salt spray testing is around 35°C (95°F). This temperature is maintained throughout the test to replicate the conditions that materials might encounter in real-world scenarios. The concentration of the salt solution is carefully monitored to ensure that it remains consistent, providing a reproducible testing environment.
The primary goal of salt spray testing is to accelerate the corrosion process to quickly evaluate the performance of materials and coatings. By exposing materials to a continuous salt mist, the test simulates the effects of prolonged exposure to salt-laden air, which can lead to rust and degradation over time. The accelerated nature of the test allows for faster assessment of a material’s resistance to corrosion compared to natural environmental exposure.
Industrial Relevance
Unlike salt fog test cabinet, salt spray testing is highly valued for its role in quality control and comparative analysis of materials and coatings. It is employed across various industries, including:
- Electronics: In the electronics industry, salt spray testing is used to ensure that components and assemblies can withstand corrosive environments, such as those encountered in marine or industrial settings. This testing helps prevent premature failure of electronic devices due to corrosion.
- Construction: For the construction industry, salt spray tests evaluate the durability of building materials and coatings that are exposed to harsh weather conditions. This includes evaluating the performance of protective coatings on metal structures and infrastructure.
- Consumer Goods: Manufacturers of consumer products, such as appliances and automotive parts, use salt spray testing to ensure their products can endure corrosive conditions, enhancing their reliability and longevity.
Choosing the Right Equipment
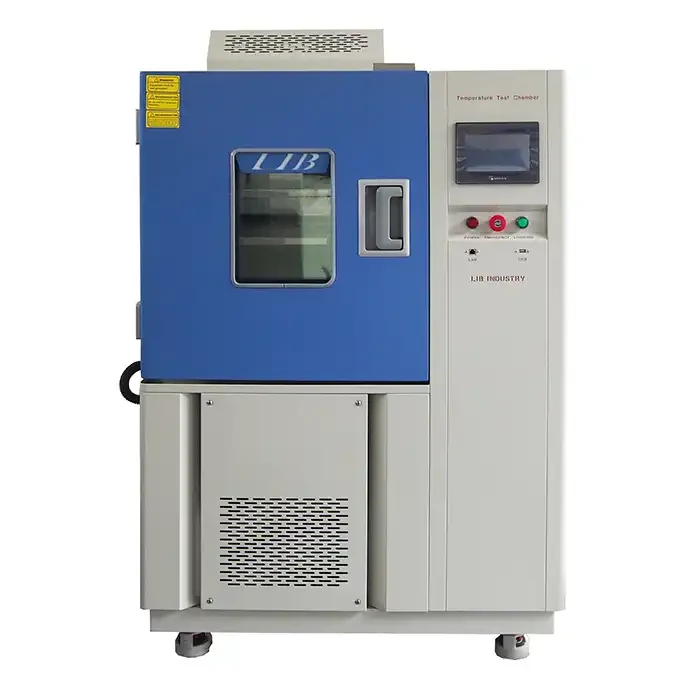
Selecting the appropriate salt spray test cabinet is crucial for obtaining accurate and consistent results. When choosing a supplier for salt spray test cabinets, consider the following features:
- Automated Control Systems: High-quality test cabinets should include automated control systems that allow for precise regulation of temperature, humidity, and salt solution concentration.
- Durable Construction: The construction of the test cabinet should be robust and resistant to corrosion itself.
- Ease of Use: The test cabinet should have a user-friendly interface that facilitates easy setup and operation.
- Consistent Results: Ensure that the equipment is capable of delivering consistent and repeatable results.
How Do Salt Fog and Salt Spray Tests Compare?
When evaluating materials for corrosion resistance, both salt fog and salt spray tests offer valuable insights. However, understanding how these two testing methods compare can help you select the most appropriate test for your specific needs. Each method has distinct characteristics, applications, and implications for how materials respond to corrosive environments.
Methodology Differences
The primary distinction between salt fog and salt spray tests lies in their approach to simulating corrosive conditions:
- Salt Fog Testing: This method creates a humid, saline environment using a fine mist of salt solution. In a salt fog test cabinet, the test specimens are exposed to a fog-like mist generated by atomizing a salt solution, typically with a concentration of 5% sodium chloride (NaCl). The environment in the chamber is maintained at a temperature around 35°C (95°F) with high humidity levels, usually around 95%.
- Salt Spray Testing: Also known as salt spray or salt mist testing, this method involves a direct spray of salt solution onto the test specimens. In salt spray tests, the solution is dispersed in a more forceful and direct manner than in salt fog tests. The solution is typically sprayed at a rate that maintains a constant exposure of approximately 5% NaCl. The standard temperature for salt spray testing is also around 35°C (95°F), but the intensity of the spray creates a more aggressive corrosive environment.
Suitability and Application
The choice between salt fog and salt spray testing depends on the specific objectives and requirements of the testing:
- Salt Fog Tests: These tests are well-suited for long-term durability studies. They are ideal for assessing materials and coatings that will experience varying environmental conditions over extended periods. The results from salt fog tests provide insights into how well materials and coatings can perform in realistic, long-term conditions.
- Salt Spray Tests: Salt spray tests are often employed for quick assessments and comparative studies. This method is particularly useful in quality control processes where fast and reliable data is needed. The more aggressive nature of salt spray tests makes them suitable for detecting issues in coatings and materials that may fail under severe conditions.
Making an Informed Decision
When choosing between salt fog and salt spray tests, consider the following factors to make an informed decision:
- Objective of Testing: Determine whether you need to evaluate long-term durability or conduct rapid assessments. If your goal is to understand how materials will perform over an extended period, salt fog testing provides a more representative simulation of long-term exposure. For immediate feedback and comparison of material performance, salt spray testing offers faster and more intense results.
- Type of Material: Consider the type of material or coating being tested. Materials exposed to moderate and variable environmental conditions may benefit more from salt fog testing, while those subject to aggressive conditions may require salt spray testing.
- Industry Requirements: Assess the specific requirements of your industry. Some industries may have established standards that dictate the type of test to be used. Understanding these requirements can help ensure compliance and relevance of the test results.
- Testing Conditions: Evaluate the conditions that best simulate the real-world environment where the material or coating will be used. Choosing the test that aligns with these conditions will provide the most meaningful and applicable results.
Conclusion
In summary, while salt fog and salt spray tests both aim to evaluate corrosion resistance, they do so in distinct ways and serve different purposes. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the right testing method and equipment for your needs. Whether you are a manufacturer, researcher, or product developer, choosing reputable salt fog test cabinet suppliers can ensure the accuracy and reliability of your corrosion testing processes.
If you have any questions or need further information, feel free to contact us at info@libtestchamber.com.
References
1. ASTM B117-19: Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog). Apparatus ASTM International.
2. ISO 9227:2017 - Corrosion Tests in Artificial Atmospheres - Salt Spray Tests. International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
3. "Salt Fog and Salt Spray Testing: A Review of Techniques and Applications". Journal of Coatings Technology and Research.
4. "Corrosion Testing of Coatings Using Salt Spray and Salt Fog Chambers". Corrosion Reviews.
5. "Evaluation of Corrosion Resistance of Materials Using Salt Spray Testing: Best Practices and Insights". Materials Performance.