From Salt Spray to Drying Cycles: The Science Behind Cyclic Corrosion Chambers
Cyclic corrosion chambers play a pivotal role in simulating real-world environmental conditions to test the durability and performance of materials. From industries like automotive to aerospace, these chambers provide invaluable insights into corrosion resistance, enhancing product reliability and longevity. Dive into the science and precision behind these advanced testing systems.
Understanding the Key Environmental Factors Replicated in Cyclic Corrosion Chambers
Cyclic corrosion chambers are engineered to mimic a wide range of environmental factors that materials face in the real world. These factors include salt spray, high humidity, temperature fluctuations, and drying cycles. By replicating these conditions, manufacturers can study how materials degrade over time.
For example, salt spray testing exposes materials to a fine mist of saline solution to simulate marine environments. High humidity accelerates the chemical reactions that lead to rust, while temperature variations test material expansion and contraction. The alternating dry phases simulate real-world conditions where wet materials dry out, leading to crack formation or further corrosion.
By combining these factors, cyclic corrosion chambers provide more realistic and comprehensive test results than traditional salt spray testing, making them a vital tool for industries requiring robust materials.
How Alternating Wet and Dry Phases Accelerate Corrosion Mechanisms?
Alternating wet and dry cycles are key to understanding how materials corrode under stress. In real-world environments, materials are rarely exposed to a single condition. For instance, a car's undercarriage might be wet from rain and then dry out under the sun. This constant shift between wet and dry phases intensifies corrosion.
During the wet phase, moisture infiltrates microcracks or pores in the material, creating a conducive environment for oxidation. When the drying phase begins, salt residues are left behind, concentrating corrosive agents on the material's surface. Over time, these cycles lead to accelerated deterioration, revealing vulnerabilities that may not emerge in static tests.
Cyclic corrosion chambers simulate these transitions with precision, providing insights into how products perform over extended periods in diverse environments. Industries such as marine engineering and construction rely on these insights to design materials that can withstand harsh conditions.
Tailoring Salt Solutions to Simulate Diverse Corrosive Environments
The versatility of cyclic corrosion chambers lies in their ability to replicate specific environmental conditions by tailoring salt solutions. Different industries face unique challenges, requiring customized testing protocols to match their needs.
For example, a manufacturer testing materials for coastal infrastructure may use a sodium chloride solution with higher concentrations to mimic the salinity of seawater. In contrast, automotive manufacturers might simulate road salt exposure by combining sodium chloride, calcium chloride, and magnesium chloride.
Advanced chambers also allow for the introduction of acidic or alkaline solutions to replicate industrial pollution or acid rain. By adjusting solution composition, temperature, and exposure time, manufacturers can simulate realistic corrosive environments and gain actionable insights into material performance.
Optimizing Parameters for Reproducible and Reliable Cyclic Corrosion Test Results
Consistency is critical in cyclic corrosion testing. To ensure reproducible and reliable results, several parameters need to be optimized, including chamber temperature, humidity levels, spray duration, and drying times.
For example, maintaining a consistent temperature range ensures uniform material exposure, while carefully calibrated spray nozzles distribute saline solutions evenly across test specimens. Humidity control is equally vital, as fluctuations can skew results and lead to inconsistent data.
Advanced cyclic corrosion chambers, like those offered by LIB Industry, feature programmable controllers that allow users to set precise test parameters. This level of control ensures repeatability and accuracy, enabling manufacturers to benchmark materials and develop solutions that meet global standards.
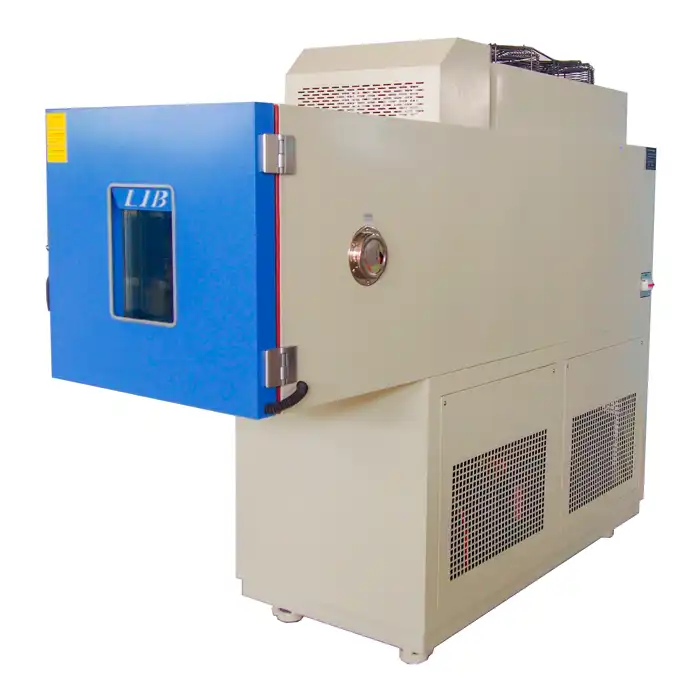
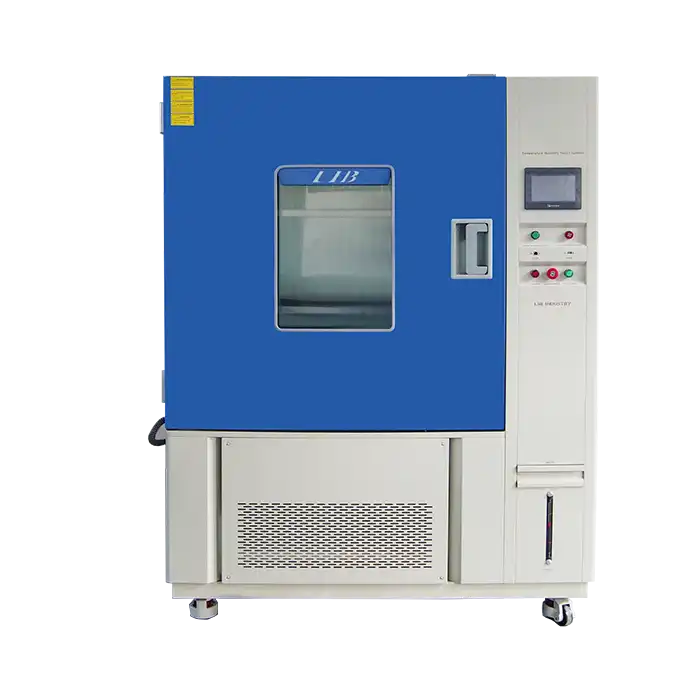
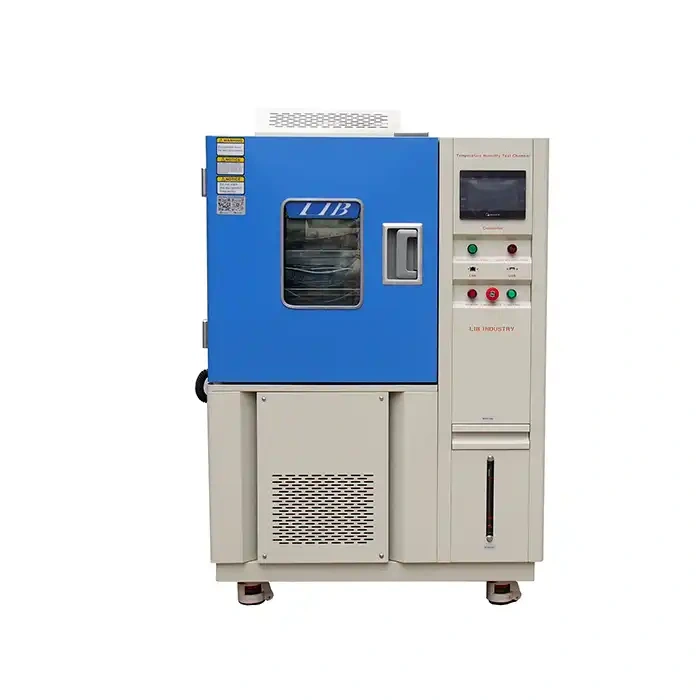
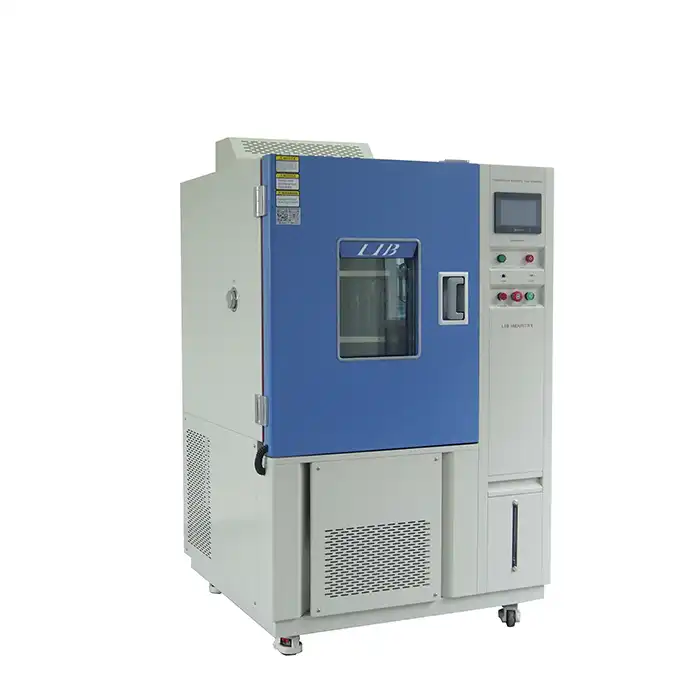
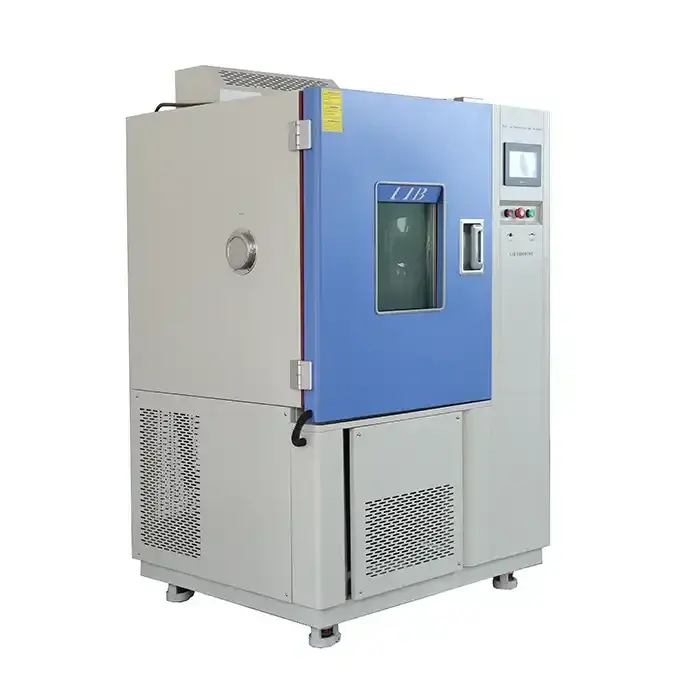
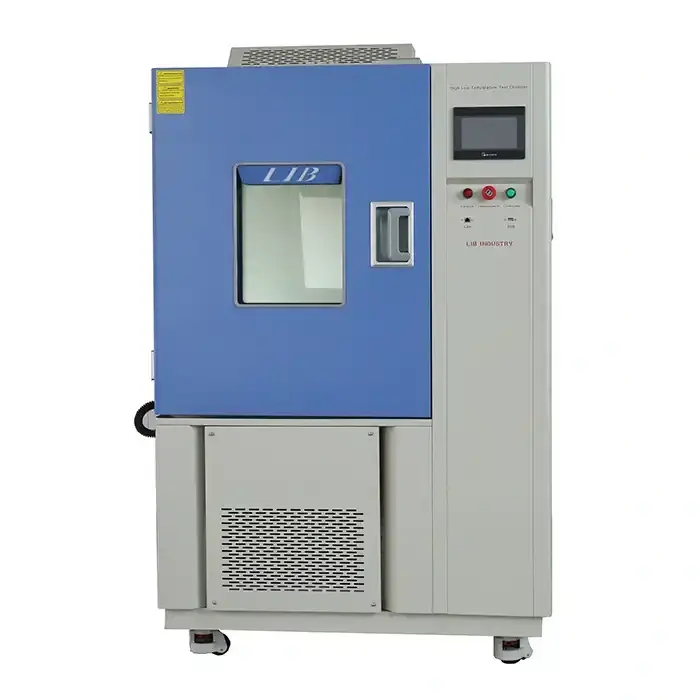
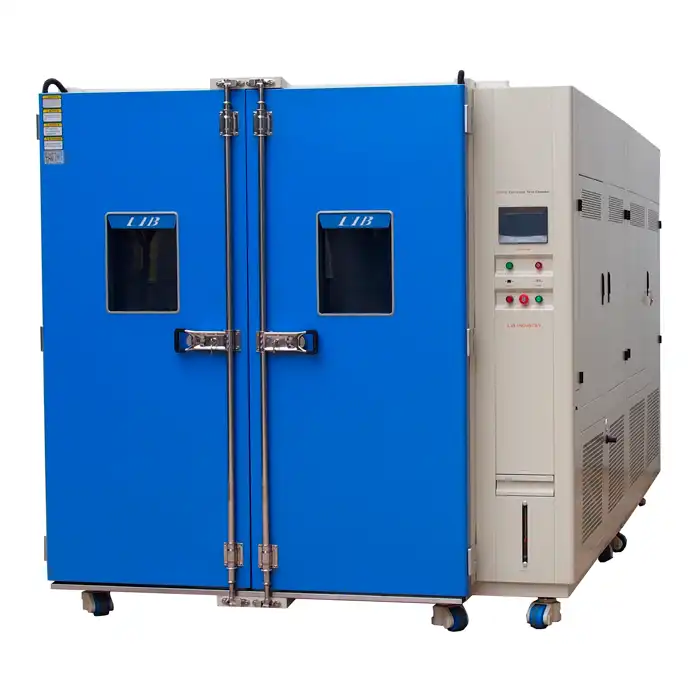
LIB Cyclic Corrosion Chamber
LIB Industry's cyclic corrosion chambers are designed to meet the most demanding testing requirements. With customizable features and cutting-edge technology, these chambers deliver reliable, reproducible results that help manufacturers tackle their toughest challenges. Key advantages of LIB's cyclic corrosion chambers:
| Temperature Range: Ambient ~ +60 ℃ Temperature Fluctuation: ± 0.5 ℃ Temperature Deviation: ± 2.0 ℃ Humidity Range: 95% ~ 98% RH Salt Fog Deposition: 1~2ml / 80cm2 · h Spray Type: Continuous / Periodic |
- Advanced Programming: LIB chambers feature intuitive touch-screen controllers, allowing users to program complex wet/dry cycles with ease.
- Customizable Testing Conditions: Simulate diverse environments with adjustable temperature, humidity, and spray parameters.
- Efficient Design: Energy-efficient systems minimize operating costs while maximizing performance.
- Durability: Built with corrosion-resistant materials for long-term reliability.
- Compliance with Standards: Designed to meet global testing standards, including ISO 9227 and ASTM B117.
Whether you're in the automotive, aerospace, or marine industry, LIB's cyclic corrosion chambers provide a turnkey solution for environmental testing. For more information or to inquire about our products, contact us at ellen@lib-industry.com.
References
1. ASTM International. "Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus (ASTM B117)."
2. ISO. "Corrosion Tests in Artificial Atmospheres - Salt Spray Tests (ISO 9227)."
3. Jones, D. A. "Principles and Prevention of Corrosion."
4. Schütze, M., and Wieser, D. "Corrosion Resistance Testing of Materials in Simulated Environments."