Comparing Salt Fog Testing Standards: ASTM vs. ISO vs. JIS
Corrosion testing using a salt fog test machine plays a vital role in product durability and reliability in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Salt fog testing, also known as salt spray testing, evaluates how materials withstand corrosive environments. However, multiple international standards govern these tests, including ASTM B117, ISO 9227, and JIS Z 2371. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right testing method.
A Deep Dive into ASTM B117: Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus and Its Applications
ASTM B117 is one of the most widely recognized salt fog testing standards, particularly in North America. Established by ASTM International, this standard provides guidelines for creating a controlled salt-laden atmosphere to assess material corrosion resistance. The test involves exposing samples to a continuous mist of 5% sodium chloride (NaCl) solution at a temperature of 35°C.
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and marine rely on ASTM B117 testing to evaluate coatings, paints, and metal substrates. The test duration varies based on material requirements, ranging from 24 hours to over 1,000 hours. For example, automotive manufacturers use ASTM B117 to assess zinc-plated steel parts, ensuring at least 96 hours of resistance before corrosion appears.
ISO 9227 Demystified: Neutral Salt Spray, Acetic Acid Salt Spray, and Copper-Accelerated Acetic Acid Salt Spray
ISO 9227 is an internationally accepted salt fog test standard, widely used across Europe and Asia. It defines three primary test methods and specifies requirements for the salt fog test machine used in these tests:
- Neutral Salt Spray (NSS): The most common test, using a 5% NaCl solution at 35 °C, similar to ASTM B117.
- Acetic Acid Salt Spray (AASS): An aggressive test for decorative coatings, incorporating acetic acid to lower pH and accelerate corrosion.
- Copper-Accelerated Acetic Acid Salt Spray (CASS): Used for highly corrosive environments, adding copper chloride (CuCl₂) to intensify oxidation, particularly for aluminum and nickel coatings.
ISO 9227 is frequently applied in automotive, construction, and aerospace industries, where long-term durability is essential.
JIS Z 2371: Unveiling the Japanese Standard for Salt Spray Testing and Its Distinct Approaches
JIS Z 2371 is Japan's national standard for salt fog testing, closely aligning with ASTM B117 and ISO 9227 but incorporating distinct methodologies. It specifies testing conditions, procedures, and evaluation methods tailored to Japanese industry requirements.
This standard is commonly used in electronics, automotive, and marine industries, where high humidity and coastal conditions demand rigorous testing. JIS Z 2371 includes:
- A 5% NaCl solution at 35 °C, like ASTM and ISO standards.
- Post-test evaluation criteria, such as corrosion spread measurement, to assess durability beyond surface appearance.
- Humidity conditioning before and after testing, mimicking Japan's high-humidity climate.
Key Parameter Comparisons: Temperature, Solution Concentration, and Exposure Duration Across Standards
Each salt fog testing standard has unique parameter requirements. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the right salt fog test machine and ensuring the test aligns with a product's intended application.
- Temperature: ASTM B117, ISO 9227 (NSS), and JIS Z 2371 all operate at 35 °C, ensuring consistent salt fog conditions. However, ISO's AASS and CASS tests may use higher temperatures to accelerate corrosion.
- Solution Concentration: A standard 5% NaCl solution is used across ASTM, JIS, and NSS-based ISO tests. ISO's AASS and CASS methods introduce acidic components (acetic acid and copper chloride) to enhance corrosion effects.
- Exposure Duration: Test durations depend on industry requirements. For example, automotive parts under ASTM B117 may undergo testing for 96 hours, while ISO 9227's CASS test may last only 22 hours due to its aggressive nature. JIS Z 2371 often extends exposure for humid conditioning, making it ideal for electronics and marine applications.
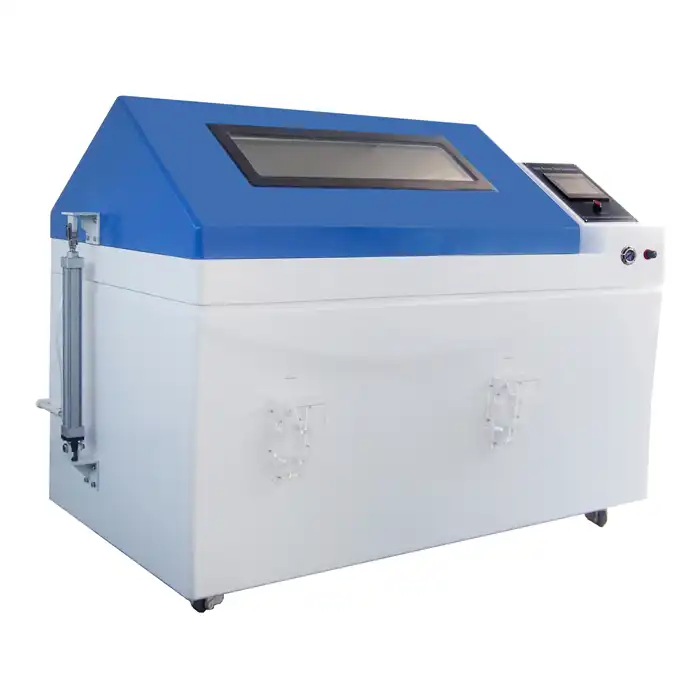
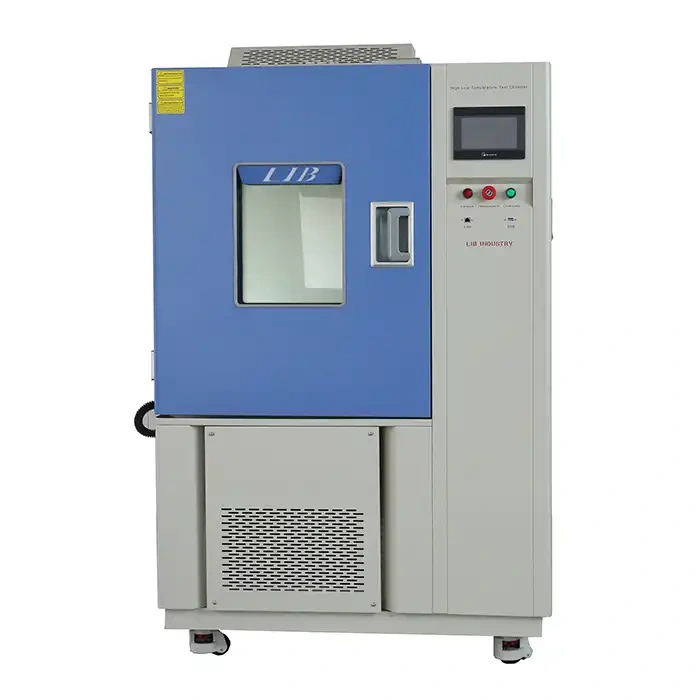
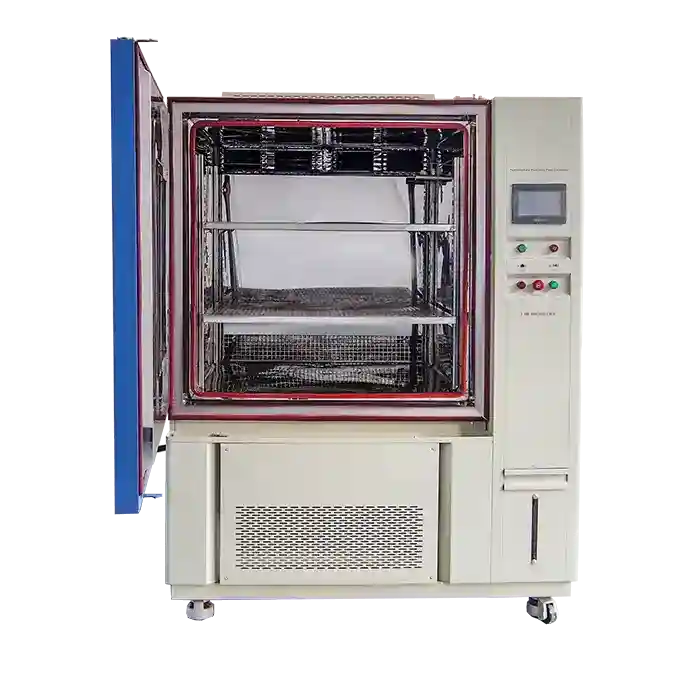
LIB Salt Fog Test Machine: Meets Multiple Test Standards
LIB Industry provides state-of-the-art salt fog test machines designed to meet ASTM, ISO, and JIS standards. These chambers offer precise environmental control, ensuring accurate and repeatable test results for diverse industries.
|
|
Key advantages of LIB's salt fog test machines include:
- Versatile Testing Capabilities: Supports ASTM B117, ISO 9227, and JIS Z 2371, making it suitable for global manufacturers.
- Advanced Humidity and Temperature Control: Ensures stable condition s for extended test durations, improving reliability.
- User-Friendly Interface: Equipped with a touchscreen controller, allowing easy test parameter adjustments.
- Durable Construction: Built from corrosion-resistant materials, ensuring longevity and minimal maintenance.
- Customizable Chamber Sizes: Available in multiple configurations, catering to small components and large industrial parts.
LIB Industry's salt fog test machines provide a turnkey solution for corrosion resistance assessments, helping businesses maintain high-quality standards across international markets. For more information, contact ellen@lib-industry.com.
References
1. ASTM International. "ASTM B117-19: Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus."
2. International Organization for Standardization. "ISO 9227:2017 Corrosion Tests in Artificial Atmospheres - Salt Spray Tests."
3. Japanese Industrial Standards Committee. "JIS Z 2371:2015 Methods of Salt Spray Testing."
4. Automotive Engineering Handbook. "Corrosion Testing and Standards for Automotive Coatings and Surface Treatments."







.webp)




