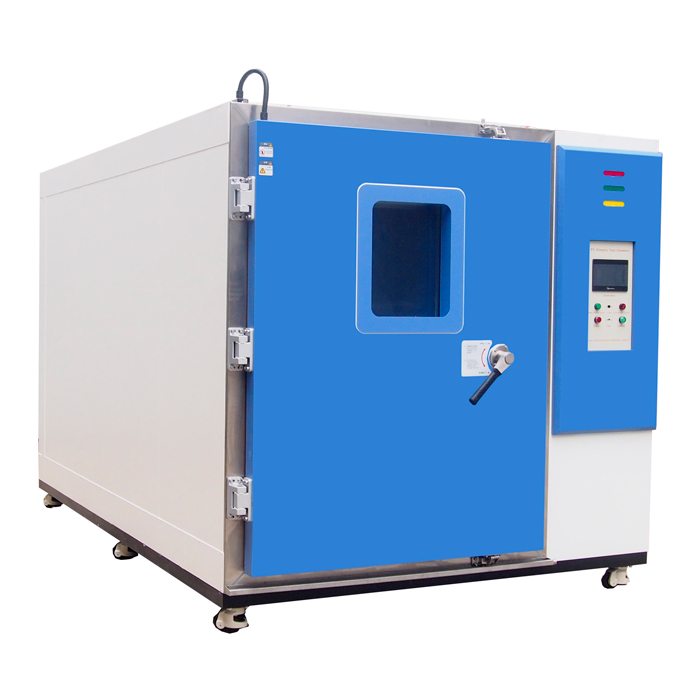
Thermal Cycling vs. Thermal Shock: What's the Difference?
When it comes to ensuring product reliability, test chambers that are often discussed are thermal cycling equipment and thermal shock chambers. Although they may sound similar, these tests serve different purposes and simulate distinct environmental challenges.
What Is Thermal Cycling? Understanding Gradual Temperature Changes
Thermal cycling is a controlled process where a product or material is gradually exposed to alternating high and low temperatures over an extended period. This test simulates real-world environmental conditions, where gradual temperature changes affect the durability and performance of materials. The goal is to identify long-term effects such as fatigue, cracking, and material weakening caused by repeated thermal expansion and contraction.
Thermal cycling is common in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where products encounter fluctuating temperatures regularly. By using thermal cycling equipment, manufacturers can assess the reliability of their products under these conditions.
What Is Thermal Shock? The Impact of Rapid Temperature Swings
Thermal shock testing involves subjecting a product to sudden and extreme temperature changes. Unlike thermal cycling, where temperature shifts happen gradually, thermal shock exposes a product to rapid changes, often within seconds. This can lead to immediate failures like cracking, warping, or delamination in materials that are sensitive to abrupt thermal stress.
Thermal shock testing is essential for products that may undergo sudden temperature changes in real-world applications, such as electronic components, medical devices, or military equipment. The test evaluates how well a product can withstand these extreme conditions without compromising its functionality or integrity.
Key Differences Between Thermal Cycling and Thermal Shock Testing
While thermal cycling equipment and thermal shock chambers both involve temperature variations, their methodologies and purposes differ significantly.
- Rate of Temperature Change: Thermal cycling involves slow, controlled temperature transitions, often taking hours to complete a cycle. In contrast, thermal shock testing exposes products to rapid temperature shifts in a matter of seconds or minutes.
- Purpose: Thermal cycling is used to simulate gradual, long-term environmental conditions that products might face over their lifespan. It's ideal for identifying material fatigue and long-term wear. Thermal shock, on the other hand, assesses a product's ability to withstand sudden and extreme temperature changes, focusing on immediate failures like cracking or delamination.
- Test Duration: Thermal cycling tests typically run for extended periods, sometimes days or weeks, as the product undergoes multiple temperature cycles. Thermal shock tests are shorter but more intense, as they subject the product to extreme conditions in a shorter time frame.
- Applications: Thermal cycling is common in industries like automotive and aerospace, where products are exposed to gradual temperature variations. Thermal shock is more relevant in sectors like electronics and defense, where products must endure rapid environmental changes.
Choosing the Right Test: When to Use Thermal Cycling vs. Thermal Shock
Selecting between thermal cycling and thermal shock depends on the intended application and the environmental conditions your product will encounter. Here are some examples to guide your decision:
- Thermal Cycling: Use thermal cycling when you need to assess long-term durability in environments with slow, seasonal temperature changes. For example, automotive components like engine parts are regularly exposed to varying temperatures as the vehicle operates in different climates. Over time, thermal cycling helps identify potential fatigue or stress fractures that could compromise safety and performance.
- Thermal Shock: Thermal shock is ideal when your product must withstand sudden and extreme temperature variations. Consider electronic components in spacecraft, which move from the warmth of Earth's atmosphere to the freezing vacuum of space within seconds. In this case, thermal shock testing ensures the product can endure those harsh, rapid transitions without failure.
In some cases, both tests may be necessary. For instance, an aerospace component might require thermal cycling to simulate the gradual temperature changes during regular operation and thermal shock testing to ensure it can survive extreme conditions during launch or re-entry.
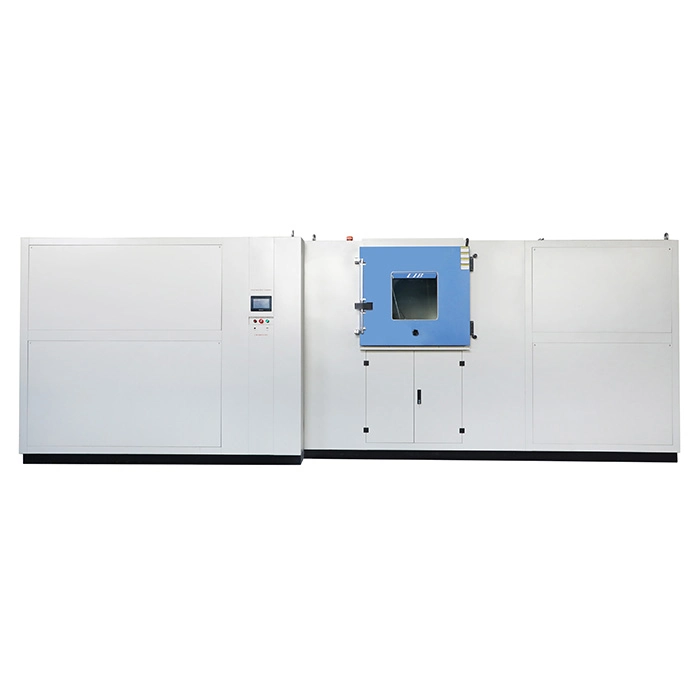
LIB Thermal Cycling Equipment
At LIB Industry, we specialize in providing advanced thermal cycling equipment designed to meet rigorous industry standards. Our thermal cycling chambers offer precise temperature control, ensuring your products undergo accurate and reliable testing. Key features of our equipment include:
- Wide Temperature Range: Our chambers can simulate a broad range of temperatures, allowing you to test products under various conditions.
- High Precision and Stability: With advanced sensors and control systems, our equipment ensures consistent and repeatable results.
- Customizable Testing Solutions: We understand that every product has unique testing requirements. That's why we offer flexible configurations to suit your specific needs, whether you're working with automotive parts, electronics, or aerospace components.
If you're looking for high-quality thermal cycling equipment, LIB Industry offers turn-key solutions tailored to your testing needs. Contact us today at ellen@lib-industry.com to learn more about our products and services.
References
1. H. Kaufmann, "Thermal Cycling vs. Thermal Shock Testing: A Comparative Study," Journal of Materials Science, 2022.
2. S. Black, "Environmental Testing in Aerospace: The Role of Thermal Cycling," Aerospace Engineering Review, 2021.
3. J. Smith, "Thermal Shock Testing for Electronics: Ensuring Durability," Electronics Reliability Quarterly, 2023.
4. A. Patel, "Material Fatigue and Thermal Cycling: Long-Term Testing Strategies," International Journal of Material Science, 2023.






.webp)


